Development and potential role of type-2 sodium-glucose transporter inhibitors for management of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 22127823
- PMCID: PMC3173594
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-011-0004-1
Development and potential role of type-2 sodium-glucose transporter inhibitors for management of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
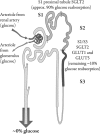
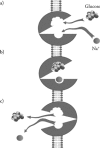
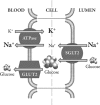
There is a recognized need for new treatment options for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Recovery of glucose from the glomerular filtrate represents an important mechanism in maintaining glucose homeostasis and represents a novel target for the management of T2DM. Recovery of glucose from the glomerular filtrate is executed principally by the type 2 sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT2). Inhibition of SGLT2 promotes glucose excretion and normalizes glycemia in animal models. First reports of specifically designed SGLT2 inhibitors began to appear in the second half of the 1990s. Several candidate SGLT2 inhibitors are currently under development, with four in the later stages of clinical testing. The safety profile of SGLT2 inhibitors is expected to be good, as their target is a highly specific membrane transporter expressed almost exclusively within the renal tubules. One safety concern is that of glycosuria, which could predispose patients to increased urinary tract infections. So far the reported safety profile of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical studies appears to confirm that the class is well tolerated. Where SGLT2 inhibitors will fit in the current cascade of treatments for T2DM has yet to be established. The expected favorable safety profile and insulin-independent mechanism of action appear to support their use in combination with other antidiabetic drugs. Promotion of glucose excretion introduces the opportunity to clear calories (80-90 g [300-400 calories] of glucose per day) in patients that are generally overweight, and is expected to work synergistically with weight reduction programs. Experience will most likely lead to better understanding of which patients are likely to respond best to SGLT2 inhibitors, and under what circumstances.
Figures

References
-
- American Diabetes Association website. Available at: http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/diabetes-statistics/?utm_source=.... Accessed 14 June 2011.
-
- American Diabetes Association. Implications of the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(Suppl.):28–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

