Secretory phospholipase A2-IIa is a target gene of the HER/HER2-elicited pathway and a potential plasma biomarker for poor prognosis of prostate cancer
- PMID: 22127954
- PMCID: PMC3345320
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.22463
Secretory phospholipase A2-IIa is a target gene of the HER/HER2-elicited pathway and a potential plasma biomarker for poor prognosis of prostate cancer
Abstract
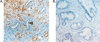
Background: Our previous study showed that prostate cancer cells overexpress and secrete secretory phospholipases A2 group IIa (sPLA2-IIa) and plasma sPLA2-IIa was elevated in prostate cancer patients. The current study further explored the underlying mechanism of sPLA2-IIa overexpression and the potential role of sPLA2-IIa as a prostate cancer biomarker.
Methods: Plasma and tissue specimens from prostate cancer patients were analyzed for sPLA2-IIa levels. Regulation of sPLA2-IIa expression by Heregulin-α was determined by Western blot and reporter assay.
Results: We found that Heregulin-α enhanced expression of the sPLA2-IIa gene via the HER2/HER3-elicited pathway. The EGFR/HER2 dual inhibitor Lapatinib and the NF-kB inhibitor Bortezomib inhibited sPLA2-IIa expression induced by Heregulin-α. Heregulin-α upregulated expression of the sPLA2-IIa gene at the transcriptional level. We further confirmed that plasma sPLA2-IIa secreted by mouse bearing human prostate cancer xenografts reached detectable plasma concentrations. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of patient plasma specimens revealed that high levels of plasma sPLA2-IIa, with the optimum cutoff value of 2.0 ng/ml, were significantly associated with high Gleason score (8-10) relative to intermediate Gleason score (6-7) prostate cancers and advanced relative to indolent cancers. The area under the ROC curve (area under curve, AUC) was 0.73 and 0.74, respectively.
Conclusion: We found that Heregulin-α, in addition to EGF, contributes to sPLA2-IIa overexpression in prostate cancer cells. Our findings support the notion that high levels of plasma sPLA2-IIa may serve as a poor prognostic biomarker capable of distinguishing aggressive from indolent prostate cancers, which may improve decision-making and optimize patient management.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

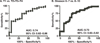

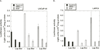
Similar articles
-
Plasma secretory phospholipase A2-IIa as a potential biomarker for lung cancer in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules.BMC Cancer. 2011 Dec 9;11:513. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-513. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22151235 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory phospholipase A2-IIa is involved in prostate cancer progression and may potentially serve as a biomarker for prostate cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Nov;31(11):1948-55. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq188. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20837598 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory phospholipase A2-IIa upregulates HER/HER2-elicited signaling in lung cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2014 Sep;45(3):978-84. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2486. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24913497 Free PMC article.
-
A Concise Update on the Relevance of Secretory Phospholipase A2 Group IIA and its Inhibitors with Cancer.Med Chem. 2017;13(7):606-615. doi: 10.2174/1573406413666170209121317. Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28185537 Review.
-
Secreted Phospholipase A2 Type IIA (sPLA2-IIA) Activates Integrins in an Allosteric Manner.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;925:103-115. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_95. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27864802 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma secretory phospholipase A2-IIa as a potential biomarker for lung cancer in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules.BMC Cancer. 2011 Dec 9;11:513. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-513. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22151235 Free PMC article.
-
Human cancer xenografts in outbred nude mice can be confounded by polymorphisms in a modifier of tumorigenesis.Genetics. 2014 Aug;197(4):1365-76. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.166587. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24913681 Free PMC article.
-
Role of 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid (20-HETE) in Androgen-Mediated Cell Viability in Prostate Cancer Cells.Horm Cancer. 2017 Aug;8(4):243-256. doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0299-0. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Horm Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28639228 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel genes that regulate androgen receptor signaling and growth of androgen-deprived prostate cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13088-104. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3743. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26036626 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Aspects of Targeting the Secreted Human Group IIA Phospholipase A2.Molecules. 2020 Sep 28;25(19):4459. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194459. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32998383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics: 2009. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2009;59(4):225–249. - PubMed
-
- USNews. Prostate cancer tests. 2010 http://healthusnewscom/usnews/health/cancer/prostate/pros_test_printhtm.
-
- Wolf AM, Wender RC, Etzioni RB, Thompson IM, D'Amico AV, Volk RJ, Brooks DD, Dash C, Guessous I, Andrews K, DeSantis C, Smith RA. American Cancer Society guideline for the early detection of prostate cancer: update 2010. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2010;60(2):70–98. - PubMed
-
- Serdar MA, Oguz O, Olgun A, Seckin B, Ilgan S, Hasimi A, Salih M, Peker F, Kutluay T. Diagnostic approach to prostate cancer using total prostate specific antigen-based parameters together. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2002;32(1):22–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

