Golimumab reduces spinal inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis: MRI results of the randomised, placebo- controlled GO-RAISE study
- PMID: 22128083
- PMCID: PMC3371220
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200308
Golimumab reduces spinal inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis: MRI results of the randomised, placebo- controlled GO-RAISE study
Erratum in
- Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 May;72(5):788
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate golimumab's effect on MRI-detected spinal inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
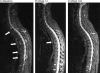
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned to subcutaneous injections of placebo (n=78), golimumab 50 mg (n=138), or golimumab 100 mg (n=140) every 4 weeks. An MRI substudy comprising 98 patients (placebo n=23, 50 mg n=37, 100 mg n=38) at eligible MRI substudy sites had serial spine MRI scans (sagittal plane, 1.5T scanners, T1 and short tau inversion recovery sequences) at baseline and weeks 14 and 104. Two blinded (treatment, image order) readers independently evaluated MRI spinal inflammation using AS spine MRI-activity (ASspiMRI-a) scores; reader scores were averaged. Changes from baseline to weeks 14 and 104 were compared among treatment groups using analysis of variance on van der Waerden normal scores both with (post-hoc) and without (prespecified) adjustment for baseline ASspiMRI-a scores.
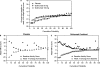
Results: Median baseline ASspiMRI-a scores were lower in the 100 mg (3.5) than placebo (6.8) and 50 mg (7.8) groups. Median decreases in activity scores from baseline to week 14 were -0.5 for placebo, -3.5 for 50 mg (p=0.047 vs placebo), and -1.5 for 100 mg (p=0.14 vs placebo). After adjusting for baseline ASspiMRI-a score imbalance, significant improvements were observed with both 50 mg (p=0.011) and 100 mg (p=0.002) versus placebo. ASspiMRI-a scores improvement achieved with golimumab was maintained at week 104. Improvement in ASspiMRI-a scores correlated with improvement in the recently developed AS disease activity score (ASDAS) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels but not with other key AS clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: Golimumab significantly reduced MRI-detected spinal inflammation of AS; improvements were sustained to week 104 and correlated with improvement in ASDAS and CRP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
[Ankylosing spondylitis--inflammation on MRI reduces long term].Rofo. 2013 May;185(5):415-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1319420. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Rofo. 2013. PMID: 23616020 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Braun J, Landewé R, Hermann KG, et al. Major reduction in spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after treatment with infliximab: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:1646–52 - PubMed
-
- Lambert RG, Salonen D, Rahman P, et al. Adalimumab significantly reduces both spinal and sacroiliac joint inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56:4005–14 - PubMed
-
- Baraliakos X, Davis J, Tsuji W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:1216–23 - PubMed
-
- Braun J, Baraliakos X, Golder W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:1126–36 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

