Pearls and pitfalls in breast MRI
- PMID: 22128131
- PMCID: PMC3473994
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/47213729
Pearls and pitfalls in breast MRI
Abstract
At our academic institution, we have noticed repeated examples of both false-positive and false-negative MR diagnoses in breast cancer. The most common diagnostic errors in interpreting MRI of the breast are discussed in this review and experience-based advice is provided to avoid similar mistakes. The most common reasons for false-positive diagnoses are misinterpretation of artefacts, confusion between normal enhancing structures and tumours and, above all, insufficient use of the American College of Radiology breast imaging reporting and data system lexicon, whereas false-negative diagnoses are made as a result of missed tiny enhancement, a background-enhancing breast, or enhancement interpreted as benign rather than malignant.
Figures

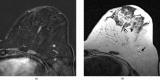
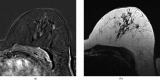
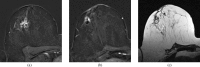
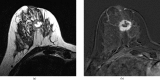
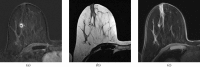
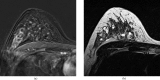
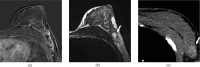

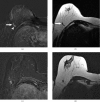
References
-
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, Harms S, Leach MO, Lehman CD, et al. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin 2007;57:75–89 Erratum in: CA Cancer J Clin 2007; 57: 185 - PubMed
-
- Liberman L, Morris EA, Dershaw DD, Abramson AF, Tan LK. MR imaging of the ipsilateral breast in women with percutaneously proven breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003;180:901–10 - PubMed
-
- Kuhl CK, Schmutzler RK, Leutner CC, Kempe A, Wardelmann E, Hocke A, et al. Breast MR imaging screening in 192 women proved or suspected to be carriers of a breast cancer susceptibility gene: preliminary results. Radiology 2000;215:267–79 - PubMed
-
- Warner E, Plewes DB, Shumak RS, Catzavelos GC, Di Prospero LS, Yaffe MJ, et al. Comparison of breast magnetic resonance imaging, mammography, and ultrasound for surveillance of women at high risk for hereditary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:3524–31 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

