Interactions between the conserved hydrophobic region of the prion protein and dodecylphosphocholine micelles
- PMID: 22128151
- PMCID: PMC3265872
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.279364
Interactions between the conserved hydrophobic region of the prion protein and dodecylphosphocholine micelles
Abstract
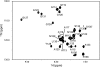
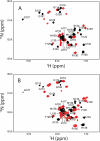
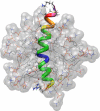
The three-dimensional structure of PrP110-136, a peptide encompassing the conserved hydrophobic region of the human prion protein, has been determined at high resolution in dodecylphosphocholine micelles by NMR. The results support the conclusion that the (Ctm)PrP, a transmembrane form of the prion protein, adopts a different conformation than the reported structures of the normal prion protein determined in solution. Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement studies with gadolinium-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid indicated that the conserved hydrophobic region peptide is not inserted symmetrically in the micelle, thus suggesting the presence of a guanidium-phosphate ion pair involving the side chain of the terminal arginine and the detergent headgroup. Titration of dodecylphosphocholine into a solution of PrP110-136 revealed the presence of a surface-bound species. In addition, paramagnetic probes located the surface-bound peptide somewhere below the micelle-water interface when using the inserted helix as a positional reference. This localization of the unknown population would allow a similar ion pair interaction.
Figures



References
-
- Will R. G., Alpers M. P., Dormont D., Schonberger L. B. (2004) Infectious and Sporadic Prion Diseases in Prion Biology and Diseases (Pruisner S. B., ed) p. 631, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
-
- Bremer J., Baumann F., Tiberi C., Wessig C., Fischer H., Schwarz P., Steele A. D., Toyka K. V., Nave K. A., Weis J., Aguzzi A. (2010) Axonal prion protein is required for peripheral myelin maintenance. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 310–318 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

