Dissection of Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling leading to matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-13) expression
- PMID: 22128168
- PMCID: PMC3256912
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.315127
Dissection of Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling leading to matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-13) expression
Abstract
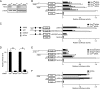
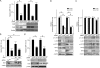
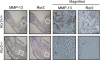
It has been shown that constitutively active Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in osteosarcoma cell lines plays crucial roles in induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13), required for their invasiveness; however, it remains largely unclear about the molecular basis of MMP-13 gene induction by Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling. Here we show by reporter assay that the activator protein 1 (AP1) (binding site in the promoter region of MMP-13 gene is primarily responsible for its transcriptional activation by Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in osteosarcoma cell lines SaOS-2 and U2OS. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays revealed that c-Jun and ATF2 are crucial transcription factors recruited to the AP1-binding site in the MMP-13 gene promoter during Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in SaOS-2 cells. Using siRNA-mediated suppression or specific inhibitors, we also show that Dishevelled2 (Dvl2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase are required for MMP-13 gene induction presumably via phosphorylation of c-Jun and ATF2 during Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in SaOS-2 cells. Interestingly, Dvl2 and Rac1, but not Dvl3, are required for MMP-13 expression in SaOS-2 cells, whereas Dvl3, but not Dvl2 and Rac1, is required for its expression in U2OS cells, indicating the presence of distinct intracellular signaling machineries leading to expression of the same gene, in this case MMP-13 gene in different osteosarcoma cell lines. Moreover, we provide evidence suggesting that Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling might also be required for expression of MMP-13 gene during the development of the cartilaginous tissue.
Figures


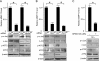

Similar articles
-
Ror2/Frizzled complex mediates Wnt5a-induced AP-1 activation by regulating Dishevelled polymerization.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(14):3610-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00177-10. Epub 2010 May 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20457807 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomous regulation of osteosarcoma cell invasiveness by Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling.Oncogene. 2009 Sep 10;28(36):3197-208. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.175. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19561643
-
Rab35 is required for Wnt5a/Dvl2-induced Rac1 activation and cell migration in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Cell Signal. 2013 May;25(5):1075-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.015. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23353182
-
Insight into the role of Wnt5a-induced signaling in normal and cancer cells.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015;314:117-48. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25619716 Review.
-
Cell/tissue-tropic functions of Wnt5a signaling in normal and cancer cells.Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Jun;20(6):346-54. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.03.001. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Trends Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20359892 Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation in osteosarcoma cells by inducing arrest in cell cycle progression.Oncol Lett. 2015 Dec;10(6):3705-3711. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3797. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26788194 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt5a Receptor, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-Like Orphan Receptor 2, Is a Predictive Cell Surface Marker of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells with an Enhanced Capacity for Chondrogenic Differentiation.Stem Cells. 2017 Nov;35(11):2280-2291. doi: 10.1002/stem.2691. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 28833807 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5A modulates integrin expression in a receptor-dependent manner in ovarian cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 15;11(1):5885. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85356-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33723319 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Ror2 mediates invasive phenotypes in renal cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 26;9(12):e116101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116101. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25542006 Free PMC article.
-
WNT5A inhibition alters the malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor microenvironment and enhances tumor growth.Oncogene. 2021 Jun;40(24):4229-4241. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01773-x. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34079083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wodarz A., Nusse R. (1998) Mechanisms of Wnt signaling in development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14, 59–88 - PubMed
-
- Logan C. Y., Nusse R. (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 781–810 - PubMed
-
- Iozzo R. V., Eichstetter I., Danielson K. G. (1995) Aberrant expression of the growth factor Wnt-5A in human malignancy. Cancer Res. 55, 3495–3499 - PubMed
-
- Weeraratna A. T., Jiang Y., Hostetter G., Rosenblatt K., Duray P., Bittner M., Trent J. M. (2002) Wnt5a signaling directly affects cell motility and invasion of metastatic melanoma. Cancer Cell 1, 279–288 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

