Structural and mechanistic insights into unusual thiol disulfide oxidoreductase
- PMID: 22128175
- PMCID: PMC3265852
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.288316
Structural and mechanistic insights into unusual thiol disulfide oxidoreductase
Abstract
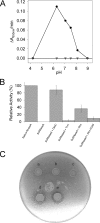
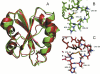
Cytoplasmic desulfothioredoxin (Dtrx) from the anaerobe Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough has been identified as a new member of the thiol disulfide oxidoreductase family. The active site of Dtrx contains a particular consensus sequence, CPHC, never seen in the cytoplasmic thioredoxins and generally found in periplasmic oxidases. Unlike canonical thioredoxins (Trx), Dtrx does not present any disulfide reductase activity, but it presents instead an unusual disulfide isomerase activity. We have used NMR spectroscopy to gain insights into the structure and the catalytic mechanism of this unusual Dtrx. The redox potential of Dtrx (-181 mV) is significantly less reducing than that of canonical Trx. A pH dependence study allowed the determination of the pK(a) of all protonable residues, including the cysteine and histidine residues. Thus, the pK(a) values for the thiol group of Cys(31) and Cys(34) are 4.8 and 11.3, respectively. The His(33) pK(a) value, experimentally determined for the first time, differs notably as a function of the redox states, 7.2 for the reduced state and 4.6 for the oxidized state. These data suggest an important role for His(33) in the molecular mechanism of Dtrx catalysis that is confirmed by the properties of mutant DtrxH33G protein. The NMR structure of Dtrx shows a different charge repartition compared with canonical Trx. The results presented are likely indicative of the involvement of this protein in the catalysis of substrates specific of the anaerobe cytoplasm of DvH. The study of Dtrx is an important step toward revealing the molecular details of the thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase catalytic mechanism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Salmonella enterica BcfH Is a Trimeric Thioredoxin-Like Bifunctional Enzyme with Both Thiol Oxidase and Disulfide Isomerase Activities.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Jul;35(1):21-39. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8218. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 33607928
-
1H, 13C and 15N backbone and side-chain chemical shift assignments for oxidized and reduced desulfothioredoxin.Biomol NMR Assign. 2010 Oct;4(2):135-7. doi: 10.1007/s12104-010-9226-9. Biomol NMR Assign. 2010. PMID: 20390383
-
The structure of the periplasmic thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase SoxS from Paracoccus pantotrophus indicates a triple Trx/Grx/DsbC functionality in chemotrophic sulfur oxidation.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009 Mar;65(Pt 3):229-40. doi: 10.1107/S0907444908043023. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009. PMID: 19237745
-
Conferring specificity in redox pathways by enzymatic thiol/disulfide exchange reactions.Free Radic Res. 2016;50(2):206-45. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1120864. Free Radic Res. 2016. PMID: 26573728 Review.
-
Enzymatic catalysis of disulfide formation.Protein Expr Purif. 1994 Feb;5(1):1-13. doi: 10.1006/prep.1994.1001. Protein Expr Purif. 1994. PMID: 7909462 Review.
Cited by
-
Measuring protein reduction potentials using 15N HSQC NMR spectroscopy.Chem Commun (Camb). 2013 Mar 4;49(18):1847-9. doi: 10.1039/c3cc38952a. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013. PMID: 23360928 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Function, Molecular Structure and Evolution of an Atypical Thioredoxin Reductase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 29;8:1855. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01855. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29033913 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine Oxidation in Proteins: Structure, Biophysics, and Simulation.Biochemistry. 2022 Oct 18;61(20):2165-2176. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00349. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Biochemistry. 2022. PMID: 36161872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two cysteines control Tse1 secretion by H1-T6SS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Protein Sci. 2025 Aug;34(8):e70226. doi: 10.1002/pro.70226. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40719405 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical Methods for Assessing Thiol Antioxidants in Biological Fluids: A Review.Molecules. 2024 Sep 18;29(18):4433. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184433. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holmgren A., Björnstedt M. (1995) Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Methods Enzymol. 252, 199–208 - PubMed
-
- Rietsch A., Beckwith J. (1998) The genetics of disulfide bond metabolism. Annu. Rev. Genet 32, 163–184 - PubMed
-
- Martin J. L. (1995) Thioredoxin: a fold for all reasons. Structure 3, 245–250 - PubMed
-
- Aslund F., Berndt K. D., Holmgren A. (1997) Redox potentials of glutaredoxins and other thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases of the thioredoxin superfamily determined by direct protein-protein redox equilibria. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30780–30786 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

