Plasmodium falciparum inhibitor-3 homolog increases protein phosphatase type 1 activity and is essential for parasitic survival
- PMID: 22128182
- PMCID: PMC3256872
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.276865
Plasmodium falciparum inhibitor-3 homolog increases protein phosphatase type 1 activity and is essential for parasitic survival
Abstract
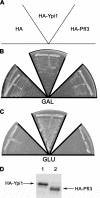
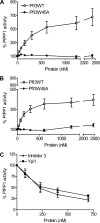
Growing evidence indicates that the protein regulators governing protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) activity have crucial functions because their deletion drastically affects cell growth and division. PP1 has been found to be essential in Plasmodium falciparum, but little is known about its regulators. In this study, we have identified a homolog of Inhibitor-3 of PP1, named PfI3. NMR analysis shows that PfI3 belongs to the disordered protein family. High affinity interaction of PfI3 and PfPP1 is demonstrated in vitro using several methods, with an apparent dissociation constant K(D) of 100 nm. We further show that the conserved (41)KVVRW(45) motif is crucial for this interaction as the replacement of the Trp(45) by an Ala(45) severely decreases the binding to PfPP1. Surprisingly, PfI3 was unable to rescue a yeast strain deficient in I3 (Ypi1). This lack of functional orthology was supported as functional assays in vitro have revealed that PfI3, unlike yeast I3 and human I3, increases PfPP1 activity. Reverse genetic approaches suggest an essential role of PfI3 in the growth and/or survival of blood stage parasites because attempts to obtain knock-out parasites were unsuccessful, although the locus of PfI3 is accessible. The main localization of a GFP-tagged PfI3 in the nucleus of all blood stage parasites is compatible with a regulatory role of PfI3 on the activity of nuclear PfPP1.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Analysis of the interactome of the Ser/Thr Protein Phosphatase type 1 in Plasmodium falciparum.BMC Genomics. 2016 Mar 17;17:246. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2571-z. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26988354 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium falciparum encodes a conserved active inhibitor-2 for Protein Phosphatase type 1: perspectives for novel anti-plasmodial therapy.BMC Biol. 2013 Jul 9;11:80. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-80. BMC Biol. 2013. PMID: 23837822 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Plasmodium falciparum inhibitor-2 motif involved in the binding and regulation activity of protein phosphatase type 1.FEBS J. 2014 Oct;281(19):4519-34. doi: 10.1111/febs.12960. Epub 2014 Sep 8. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 25132288
-
Protein phosphatase 1: life-course regulation by SDS22 and Inhibitor-3.FEBS J. 2022 Jun;289(11):3072-3085. doi: 10.1111/febs.16029. Epub 2021 Jun 13. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34028981 Review.
-
Plasmodium falciparum kelch 13: a potential molecular marker for tackling artemisinin-resistant malaria parasites.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016;14(1):125-35. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2016.1106938. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016. PMID: 26535806 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Role of Protein Phosphatases in Apicomplexa: The Future of Innovative Therapeutics?Microorganisms. 2022 Mar 8;10(3):585. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030585. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35336160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the interactome of the Ser/Thr Protein Phosphatase type 1 in Plasmodium falciparum.BMC Genomics. 2016 Mar 17;17:246. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2571-z. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26988354 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide in silico analysis of Plasmodium falciparum phosphatome.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 25;15:1024. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1024. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25425018 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Plasmodium falciparum Translation Initiation eIF2β Subunit: Direct Interaction with Protein Phosphatase Type 1.Front Microbiol. 2016 May 26;7:777. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00777. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27303372 Free PMC article.
-
PhosphoTyrosyl phosphatase activator of Plasmodium falciparum: identification of its residues involved in binding to and activation of PP2A.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Feb 11;15(2):2431-53. doi: 10.3390/ijms15022431. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24521882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berndt N. (1999) Protein dephosphorylation and the intracellular control of the cell number. Front. Biosci. 4, D22–D42 - PubMed
-
- Honkanen R. E., Zwiller J., Moore R. E., Daily S. L., Khatra B. S., Dukelow M., Boynton A. L. (1990) Characterization of microcystin-LR, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 19401–19404 - PubMed
-
- Ohta T., Sueoka E., Iida N., Komori A., Suganuma M., Nishiwaki R., Tatematsu M., Kim S. J., Carmichael W. W., Fujiki H. (1994) Nodularin, a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A, is a new environmental carcinogen in male F344 rat liver. Cancer Res. 54, 6402–6406 - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama H., Papst P., Fujita M., Gelfand E. W., Terada N. (1997) Overexpression of wild type p70 S6 kinase interferes with cytokinesis. Oncogene 15, 443–452 - PubMed
-
- Cheng A., Kaldis P., Solomon M. J. (2000) Dephosphorylation of human cyclin-dependent kinases by protein phosphatase type 2C α and β2 isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 34744–34749 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

