Gastric ulcer healing after treatment of endoscopic submucosal dissection in Japanese: comparison of H(2) receptor antagonist and proton pump inhibitor administration
- PMID: 22128222
- PMCID: PMC3208019
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.11-23
Gastric ulcer healing after treatment of endoscopic submucosal dissection in Japanese: comparison of H(2) receptor antagonist and proton pump inhibitor administration
Abstract
Endoscopic submucosal dissection has made it possible to resect large lesions during a single operation. The present study was undertaken to compare the time taken for recovery from artificial ulcers after endoscopic submucosal dissection between an H(2) Receptor Antagonist treatment group and a Proton Pump Inhibitor treatment group, focusing on analysis of the time course of reduction rate in ulcer area. The powerful acid suppression by Proton Pump Inhibitor may not be needed to treat Japanese post-endoscopic submucosal dissection ulcer which usually develops after early gastric carcinoma in the mucosa of low acid secretory capacity. The study involved 60 patients with 69 artificial ulcers following endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of tumors remaining in the gastric mucosa. Of all lesions, 36 were allocated to the H(2) Receptor Antagonist group and 33 to the Proton Pump Inhibitor group. Patients in both groups underwent endoscopy at 4 and 8 weeks after the start of administration. There were no significant differences between two groups and ulcer healing rates were similar in the two groups. The efficacy of H(2) Receptor Antagonists in curing this type of ulcer can thus be expected to be comparable to that of Proton Pump Inhibitors.
Keywords: H2 receptor antagonist; endoscopic submucosal dissection; gastric ulcer healing; proton pump inhibitor.
Figures



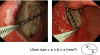
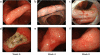
Similar articles
-
Comparison of vonoprazan and proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 15;24(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03198-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38491413 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of administration of a proton pump inhibitor before endoscopic submucosal dissection for differentiated early gastric cancer with ulcer.Gastric Cancer. 2017 Jan;20(1):200-206. doi: 10.1007/s10120-015-0578-9. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Gastric Cancer. 2017. PMID: 26661593
-
Vonoprazan is superior to proton pump inhibitors in healing artificial ulcers of the stomach post-endoscopic submucosal dissection: A propensity score-matching analysis.Dig Endosc. 2017 Jan;29(1):57-64. doi: 10.1111/den.12705. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Dig Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27492962
-
Feasibility of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection without using proton pump inhibitor injection: a propensity score analysis.J Rural Med. 2020 Jul;15(3):85-91. doi: 10.2185/jrm.2019-021. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Rural Med. 2020. PMID: 32704333 Free PMC article.
-
Proton pump inhibitor alone vs proton pump inhibitor plus mucosal protective agents for endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015 Mar;56(2):85-90. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.14-101. Epub 2014 Dec 27. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25759512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy before and after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Review.Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012;2012:791873. doi: 10.1155/2012/791873. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012. PMID: 22851882 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of proton pump inhibitor and rebamipide, a free radical scavenger, promotes artificial ulcer healing after endoscopic submucosal dissection with dissection size >40 mm.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012 Nov;51(3):185-8. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.12-14. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012. PMID: 23170045 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome and risk factors of ulcer healing after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Nov 27;16(11):3568-3577. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i11.3568. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 39649187 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of a newly designed self-assembling gel in the treatment of endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced gastric ulcer: A multicenter randomized controlled trial.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1002381. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1002381. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36532761 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Effects of Vonoprazan and Lansoprazole for Treating Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection-Induced Artificial Ulcers.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Apr;63(4):974-981. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-4948-0. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29464587 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Tada M, Murakami A, Karita M, Yanani H, Okita K. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 1993;25:445–450. - PubMed
-
- Hirao M, Masuda K, Asanuma T, et al. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer and other tumors with local injection of hypertonic saline-epinephrine. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988;34:264–269. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi Y, Katsumi N, Tauchi M, et al. A prospective randomized trial of either famotidine or omeprazole for the prevention of bleeding after endoscopic mucosal resection and the healing of endoscopic mucosal resection-induced ulceration. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;21(Suppl 2):111–115. - PubMed
-
- Lee SY, Kim JJ, Lee JH, et al. Healing rate of EMR-induced ulcer in relation to the duration of treatment with omeprazole. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:213–217. - PubMed
-
- Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Boku N, Ohtu A, Tajiri H, Yoshida S. New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy. 2001;33:221–226. - PubMed

