Molecular genetic analysis of retinitis pigmentosa in Indonesia using genome-wide homozygosity mapping
- PMID: 22128245
- PMCID: PMC3224842
Molecular genetic analysis of retinitis pigmentosa in Indonesia using genome-wide homozygosity mapping
Abstract
Purpose: Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous retinal disorder. Despite tremendous knowledge about the genes involved in RP, little is known about the genetic causes of RP in Indonesia. Here, we aim to identify the molecular genetic causes underlying RP in a small cohort of Indonesian patients, using genome-wide homozygosity mapping.
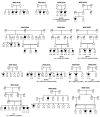
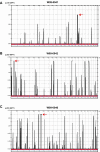
Methods: DNA samples from affected and healthy individuals from 14 Indonesian families segregating autosomal recessive, X-linked, or isolated RP were collected. Homozygosity mapping was conducted using Illumina 6k or Affymetrix 5.0 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays. Known autosomal recessive RP (arRP) genes residing in homozygous regions and X-linked RP genes were sequenced for mutations.
Results: In ten out of the 14 families, homozygous regions were identified that contained genes known to be involved in the pathogenesis of RP. Sequence analysis of these genes revealed seven novel homozygous mutations in ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A, member 4 (ABCA4), crumbs homolog 1 (CRB1), eyes shut homolog (Drosophila) (EYS), c-mer proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase (MERTK), nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group E, member 3 (NR2E3) and phosphodiesterase 6A, cGMP-specific, rod, alpha (PDE6A), all segregating in the respective families. No mutations were identified in the X-linked genes retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (RPGR) and retinitis pigmentosa 2 (X-linked recessive; RP2).
Conclusions: Homozygosity mapping is a powerful tool to identify the genetic defects underlying RP in the Indonesian population. Compared to studies involving patients from other populations, the same genes appear to be implicated in the etiology of recessive RP in Indonesia, although all mutations that were discovered are novel and as such may be unique for this population.
Figures
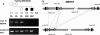

Similar articles
-
Identification of mutations causing inherited retinal degenerations in the israeli and palestinian populations using homozygosity mapping.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Feb 24;55(2):1149-60. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13625. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24474277
-
Homozygosity mapping in autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa families detects novel mutations.Mol Vis. 2013 Dec 8;19:2487-500. eCollection 2013. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 24339724 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in TULP1, NR2E3, and MFRP genes in Indian families with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa.Mol Vis. 2012;18:1165-74. Epub 2012 May 4. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 22605927 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the molecular genetics of retinitis pigmentosa.Ophthalmic Genet. 2001 Sep;22(3):133-54. doi: 10.1076/opge.22.3.133.2224. Ophthalmic Genet. 2001. PMID: 11559856 Review.
-
Nonsyndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa Overview.2000 Aug 4 [updated 2023 Apr 6]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2000 Aug 4 [updated 2023 Apr 6]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301590 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
MERTK controls melanoma cell migration and survival and differentially regulates cell behavior relative to AXL.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 Jul;26(4):527-41. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12110. Epub 2013 May 21. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23617806 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Novel Mutation in the ABCA4 Gene in a Chinese Family with Retinitis Pigmentosa Using Exome Sequencing.Biosci Rep. 2018 Apr 27;38(2):BSR20171300. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171300. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29437900 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Genetic Analysis of the Autosomal Recessive Non-Syndromic Inherited Retinitis Pigmentosa.Cureus. 2023 Apr 21;15(4):e37933. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37933. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37267051 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygosity mapping reveals novel and known mutations in Pakistani families with inherited retinal dystrophies.Sci Rep. 2015 May 6;5:9965. doi: 10.1038/srep09965. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25943428 Free PMC article.
-
Novel variants in PDE6A and PDE6B genes and its phenotypes in patients with retinitis pigmentosa in Chinese families.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Jan 15;22(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02242-5. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35033039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berson EL. Retinitis pigmentosa. The Friedenwald Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993;34:1659–76. - PubMed
-
- Berger W, Kloeckener-Gruissem B, Neidhardt J. The molecular basis of human retinal and vitreoretinal diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010;29:335–75. - PubMed
-
- Bandah-Rozenfeld D, Collin RW, Banin E, van den Born LI, Coene KL, Siemiatkowska AM, Zelinger L, Khan MI, Lefeber DJ, Erdinest I, Testa F, Simonelli F, Voesenek K, Blokland EA, Strom TM, Klaver CC, Qamar R, Banfi S, Cremers FP, Sharon D, den Hollander AI. Mutations in IMPG2, encoding interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglycan 2, cause autosomal-recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 2010;87:199–208. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collin RW, Littink KW, Klevering BJ, van den Born LI, Koenekoop RK, Zonneveld MN, Blokland EA, Strom TM, Hoyng CB, den Hollander AI, Cremers FP. Identification of a 2 Mb human ortholog of Drosophila eyes shut/spacemaker that is mutated in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;83:594–603. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
