Exploration of sex differences in Rhes effects in dopamine mediated behaviors
- PMID: 22128255
- PMCID: PMC3225344
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S25888
Exploration of sex differences in Rhes effects in dopamine mediated behaviors
Abstract
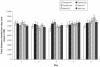
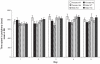
Studies have shown that Ras homolog enriched in striatum (Rhes) proteins are highly expressed in areas of the central nervous system that have high dopaminergic innervation. In this study, we used Rhes mutant mice (Wild type, Rhes KO, Rhes Heterozygous) of both sexes to explore differences in the effects of Rhes protein levels in basal levels of activity, anxiety, and stereotypy, in relation to sex. Adult male and female mice were evaluated in an open field test for measuring basal levels of activity and anxiety for 5 consecutive days, and they were tested in the apomorphine-induced stereotypy paradigm. Rhes protein levels affected basal levels of activity but it was not found to be related to sex differences. Moreover, a decrease in Rhes protein levels was linked to a nonsignificant anxiolytic effect, mainly in female mice. Finally, a decrease in Rhes protein levels does not affect dopamine D(1) and D(2) receptor (D(1)/D(2)) synergism in female or male mice. Together, these results suggest that Rhes protein levels affect locomotion activity, and have an influence in anxiety depending on sex; Rhes protein levels do not affect D(1)/D(2) synergism in both sexes.
Keywords: Rhes protein; behavior; dopamine receptor; mutant mice; sexes.
Figures
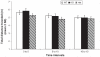
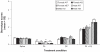
References
-
- Goldman-Rakic PS, Selemon LD. New frontiers in basal ganglia research. Introduction. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13(7):241–244. - PubMed
-
- Sibley DR, Monsma FJ., Jr Molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992;13(2):61–69. - PubMed
-
- O’Sullivan GJ, Kinsella A, Grandy DK, Tighe O, Croke DT, Waddington JL. Ethological resolution of behavioral topography and D2-like vs D1-like agonist responses in congenic D4 dopamine receptor “knockouts”: identification of D4:D1-like interactions. Synapse. 2006;59(2):107–118. - PubMed
-
- Braun AR, Chase TN. Obligatory D-1/D-2 receptor interaction in the generation of dopamine agonist related behaviors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986;131(2–3):301–306. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

