Quercetin-induced Growth Inhibition in Human Bladder Cancer Cells Is Associated with an Increase in Ca-activated K Channels
- PMID: 22128260
- PMCID: PMC3222797
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.5.279
Quercetin-induced Growth Inhibition in Human Bladder Cancer Cells Is Associated with an Increase in Ca-activated K Channels
Abstract
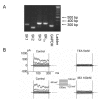
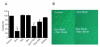
Quercetin (3,3',4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavone) is an attractive therapeutic flavonoid for cancer treatment because of its beneficial properties including apoptotic, antioxidant, and antiproliferative effects on cancer cells. However, the exact mechanism of action of quercetin on ion channel modulation is poorly understood in bladder cancer 253J cells. In this study, we demonstrated that large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK(Ca)) or MaxiK channels were functionally expressed in 253J cells, and quercetin increased BK(Ca) current in a concentration dependent and reversible manner using a whole cell patch configuration. The half maximal activation concentration (IC(50)) of quercetin was 45.5±7.2 µM. The quercetin-evoked BK(Ca) current was inhibited by tetraethylammonium (TEA; 5 mM) a non-specific BK(Ca) blocker and iberiotoxin (IBX; 100 nM) a BK(Ca)-specific blocker. Quercetin-induced membrane hyperpolarization was measured by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) with voltage sensitive dye, bis (1,3-dibutylbarbituric acid) trimethine oxonol (DiBAC(4)(3); 100 nM). Quercetin-evoked hyperpolarization was prevented by TEA. Quercetin produced an antiproliferative effect (30.3±13.5%) which was recovered to 53.3±10.5% and 72.9±3.7% by TEA and IBX, respectively. Taken together our results indicate that activation of BK(Ca) channels may be considered an important target related to the action of quercetin on human bladder cancer cells.
Keywords: BKCa; Bladder cancer cell; Proliferation; Quercetin; Voltage sensitive dye.
Figures

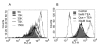
Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide (NO)-induced activation of large conductance Ca2+-dependent K+ channels (BK(Ca)) in smooth muscle cells isolated from the rat mesenteric artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jul;124(6):1131-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701940. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9720783 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of SK and BK channels by Ca(2+) signals from Ca(2+) channels and ryanodine receptors in guinea-pig urinary bladder myocytes.J Physiol. 2002 Jun 1;541(Pt 2):483-92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.017707. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12042353 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin-induced induction of the NO/cGMP pathway depends on Ca2+-activated K+ channel-induced hyperpolarization-mediated Ca2+-entry into cultured human endothelial cells.Planta Med. 2005 Jun;71(6):520-4. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-864152. Planta Med. 2005. PMID: 15971122
-
Neuroregulation of mucus secretion by opioid receptors and K(ATP) and BK(Ca) channels in ferret trachea in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;123(8):1631-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701786. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9605570 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K (+) channel in laminar shear stress-induced inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.Pflugers Arch. 2013 Feb;465(2):221-32. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1182-z. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 23179380
Cited by
-
The Green Anti-Cancer Weapon. The Role of Natural Compounds in Bladder Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 21;22(15):7787. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157787. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin induces bladder cancer cells apoptosis by activation of AMPK signaling pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 15;6(2):498-508. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27186419 Free PMC article.
-
The cross-correlation-based analysis to digest the conformational dynamics of the mitoBK channels in terms of their modulation by flavonoids.Eur Biophys J. 2023 Oct;52(6-7):569-582. doi: 10.1007/s00249-023-01666-9. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Eur Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37389670 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of ECQ on Rat Reflux Esophagitis Model.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;16(6):455-62. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.6.455. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23269908 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Combination of Quercetin and Mafosfamide in Treatment of Bladder Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2024 Oct 31;29(21):5176. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215176. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirpara KV, Aggarwal P, Mukherjee AJ, Joshi N, Burman AC. Quercetin and its derivatives: synthesis, pharmacological uses with special emphasis on anti-tumor properties and prodrug with enhanced bio-availability. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2009;9:138–161. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto T. Safety of quercetin for clinical application (Review) Int J Mol Med. 2005;16:275–278. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz MJ, Fernández M, Picó Y, Mañes J, Asensi M, Carda C, Asensio G, Estrela JM. Dietary administration of high doses of pterostilbene and quercetin to mice is not toxic. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:3180–3186. - PubMed
-
- Avila MA, Velasco JA, Cansado J, Notario V. Quercetin mediates the down-regulation of mutant p53 in the human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB468. Cancer Res. 1994;54:2424–2428. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Kim SK, Kim BS, Lee SH, Park YS, Park BK, Kim SJ, Kim J, Choi C, Kim JS, Cho SD, Jung JW, Roh KH, Kang KS, Jung JY. Apoptotic effect of quercetin on HT-29 colon cancer cells via the AMPK signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58:8643–8650. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

