The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, ETC-642, reduces chronic vascular inflammation in the rabbit
- PMID: 22128776
- PMCID: PMC3276454
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-224
The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, ETC-642, reduces chronic vascular inflammation in the rabbit
Abstract
Background: High-density lipoproteins (HDL) and their main apolipoprotein, apoA-I, exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. The development of peptides that mimic HDL apolipoproteins offers a promising strategy to reduce inflammatory disease. This study aimed to compare the anti-inflammatory effects of ETC-642, an apoA-I mimetic peptide, with that of discoidal reconstituted HDL (rHDL), consisting of full-length apoA-I complexed with phosphatidylcholine, in rabbits with chronic vascular inflammation.
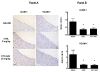
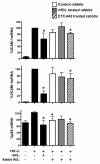
Results: New Zealand White rabbits (n = 10/group) were placed on chow supplemented with 0.2% (w/w) cholesterol for 6-weeks. The animals received two infusions of saline, rHDL (8 mg/kg apoA-I) or ETC-642 (30 mg/kg peptide) on the third and fifth days of the final week. The infusions of rHDL and ETC-642 were able to significantly reduce cholesterol-induced expression of intracellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in the thoracic aorta (p < 0.05). When isolated rabbit HDL was pre-incubated with human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs), prior to stimulation with TNF-α, it was found that HDL from ETC-642 treated rabbits were more effective at inhibiting the TNF-α-induced increase in ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and p65 than HDL isolated from saline treated rabbits (p < 0.05). There were, however, no changes in HDL lipid composition between treatment groups.
Conclusions: Infusion of ETC-642 causes anti-inflammatory effects that are comparable to rHDL in an animal model of chronic vascular inflammation and highlights that apoA-I mimetic peptides present a viable strategy for the treatment of inflammatory disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide ETC-642 exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that are comparable to high density lipoproteins.Atherosclerosis. 2011 Aug;217(2):395-400. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.04.001. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21571275
-
The 5A apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide displays antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties in vivo and in vitro.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Feb;30(2):246-52. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200196. Epub 2009 Dec 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 19965776 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of apolipoprotein A-I in the rabbit.Atherosclerosis. 2010 Oct;212(2):392-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.05.035. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Atherosclerosis. 2010. PMID: 20609437
-
Inhibition of Vascular Inflammation by Apolipoprotein A-IV.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 30;9:901408. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.901408. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35845068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human apolipoprotein A-I and A-I mimetic peptides: potential for atherosclerosis reversal.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2004 Dec;15(6):645-9. doi: 10.1097/00041433-200412000-00004. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2004. PMID: 15529023 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational Design and In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of an ApoE-Based Synthetic High-Density Lipoprotein for Sepsis Therapy.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 11;15(3):397. doi: 10.3390/biom15030397. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149933 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein Mimetic Peptides: Potential New Therapies for Cardiovascular Diseases.Cells. 2021 Mar 8;10(3):597. doi: 10.3390/cells10030597. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33800446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecules that mimic apolipoprotein A-I: potential agents for treating atherosclerosis.J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 27;57(6):2169-96. doi: 10.1021/jm4005847. Epub 2013 Oct 29. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24168751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDL and Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1377:171-187. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-1592-5_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35575930
-
Antioxidative activity of high-density lipoprotein (HDL): Mechanistic insights into potential clinical benefit.BBA Clin. 2017 Aug 19;8:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2017.07.002. eCollection 2017 Dec. BBA Clin. 2017. PMID: 28936395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nicholls SJ, Dusting GJ, Cutri B, Bao S, Drummond GR, Rye KA, Barter PJ. Reconstituted high-density lipoproteins inhibit the acute pro-oxidant and proinflammatory vascular changes induced by a periarterial collar in normocholesterolemic rabbits. Circulation. 2005;111:1543–1550. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000159351.95399.50. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

