Interaction of 3β-amino-5-cholestene with phospholipids in binary and ternary bilayer membranes
- PMID: 22128897
- PMCID: PMC3265605
- DOI: 10.1021/la203589u
Interaction of 3β-amino-5-cholestene with phospholipids in binary and ternary bilayer membranes
Abstract
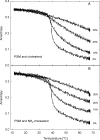
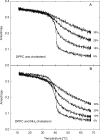
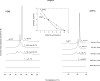
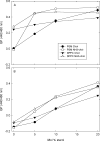
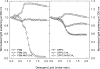
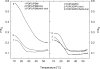
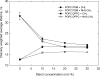
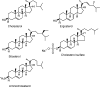
3β-Amino-5-cholestene (aminocholesterol) is a synthetic sterol whose properties in bilayer membranes have been examined. In fluid palmitoyl sphingomyelin (PSM) bilayers, aminocholesterol and cholesterol were equally effective in increasing acyl chain order, based on changes in diphenylhexatriene (DPH) anisotropy. In fluid 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) bilayers, aminocholesterol ordered acyl chains, but slightly less efficiently than cholesterol. Aminocholesterol eliminated the PSM and DPPC gel-to-liquid crystalline phase transition enthalpy linearly with concentration, and the enthalpy approached zero at 30 mol % sterol. Whereas cholesterol was able to increase the thermostability of ordered PSM domains in a fluid bilayer, aminocholesterol under equal conditions failed to do this, suggesting that its interaction with PSM was not as favorable as cholesterols. In ternary mixed bilayers, containing 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC), PSM or DPPC, and cholesterol at proportions to contain a liquid-ordered phase (60:40 by mol of POPC and PSM or DPPC, and 30 mol % cholesterol), the average lifetime of trans-parinaric acid (tPA) was close to 20 ns. When cholesterol was replaced with aminocholesterol in such mixed bilayers, the average lifetime of tPA was only marginally shorter (about 18 ns). This observation, together with acyl chain ordering data, clearly shows that aminocholesterol was able to form a liquid-ordered phase with saturated PSM or DPPC. We conclude that aminocholesterol should be a good sterol replacement in model membrane systems for which a partial positive charge is deemed beneficial.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

