The fine specificity of IgM anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) is different from that of IgG ACPA
- PMID: 22129077
- PMCID: PMC3334645
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3524
The fine specificity of IgM anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) is different from that of IgG ACPA
Abstract
Introduction: The antigen recognition pattern of immunoglobulin M (IgM) could, when directed against protein antigens, provide an indication of the antigenic moieties triggering new B cells. The half-life of IgM is short and memory B cells against T-cell-dependent protein antigens typically produce IgG and not IgM antibodies. In this study, we analyzed whether a difference exists between the fine specificity of IgM versus IgG anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs).
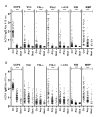
Methods: We determined the fine specificity of IgM and IgG ACPAs in 113 ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients with IgM cyclic citrullinated peptide 2 (CCP2) levels above 100 AU/ml. Fine specificity was assessed by performing ELISA using citrullinated peptides derived from vimentin, fibrinogen-β, fibrinogen-α and α-enolase, as well as citrullinated proteins fibrinogen and myelin basic protein. The arginine counterparts were used as controls.
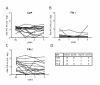
Results: Recognition of defined citrullinated antigens by IgM ACPA was confined to samples that also displayed recognition by IgG ACPA. However, the IgM ACPA response displayed a more restricted antigen recognition profile than IgG ACPA (OR = 0.26, P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Our data show that several defined citrullinated antigens are recognized only by IgG ACPA, whereas others are also recognized by IgM ACPA. These observations suggest that not all citrullinated antigens are able to activate new B cells despite concurrent recognition by IgG ACPA.
Figures

References
-
- van Venrooij WJ, Hazes JM, Visser H. Anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibody and its role in the diagnosis and prognosis of early rheumatoid arthritis. Neth J Med. 2002;60:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Nielen MM, van der Horst AR, van Schaardenburg D, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van de Stadt RJ, Aarden L, Dijkmans BA, Hamann D. Antibodies to citrullinated human fibrinogen (ACF) have diagnostic and prognostic value in early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:1199–1204. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.029389. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clavel C, Nogueira L, Laurent L, Iobagiu C, Vincent C, Sebbag M, Serre G. Induction of macrophage secretion of tumor necrosis factor α through Fcγ receptor IIa engagement by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies to citrullinated proteins complexed with fibrinogen. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:678–688. doi: 10.1002/art.23284. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

