13-hydroxy linoleic acid increases expression of the cholesterol transporters ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI and stimulates apoA-I-dependent cholesterol efflux in RAW264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 22129452
- PMCID: PMC3248880
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-222
13-hydroxy linoleic acid increases expression of the cholesterol transporters ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI and stimulates apoA-I-dependent cholesterol efflux in RAW264.7 macrophages
Abstract
Background: Synthetic activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) stimulate cholesterol removal from macrophages through PPAR-dependent up-regulation of liver × receptor α (LXRα) and subsequent induction of cholesterol exporters such as ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-BI). The present study aimed to test the hypothesis that the hydroxylated derivative of linoleic acid (LA), 13-HODE, which is a natural PPAR agonist, has similar effects in RAW264.7 macrophages.
Methods: RAW264.7 macrophages were treated without (control) or with LA or 13-HODE in the presence and absence of PPARα or PPARγ antagonists and determined protein levels of LXRα, ABCA1, ABCG1, SR-BI, PPARα and PPARγ and apolipoprotein A-I mediated lipid efflux.
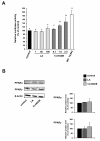
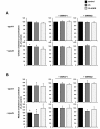
Results: Treatment of RAW264.7 cells with 13-HODE increased PPAR-transactivation activity and protein concentrations of LXRα, ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI when compared to control treatment (P < 0.05). In addition, 13-HODE enhanced cholesterol concentration in the medium but decreased cellular cholesterol concentration during incubation of cells with the extracellular lipid acceptor apolipoprotein A-I (P < 0.05). Pre-treatment of cells with a selective PPARα or PPARγ antagonist completely abolished the effects of 13-HODE on cholesterol efflux and protein levels of genes investigated. In contrast to 13-HODE, LA had no effect on either of these parameters compared to control cells.
Conclusion: 13-HODE induces cholesterol efflux from macrophages via the PPAR-LXRα-ABCA1/SR-BI-pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Liu JF, Huang CJ. Tissue α-tocopherol retention in male rats is compromised by feeding diets containing oxidized frying oil. J Nutr. 1995;125:3071–3080. - PubMed
-
- Eder K, Keller U, Hirche F, Brandsch C. Thermally oxidized dietary fats increase the susceptibility of rat LDL to lipid peroxidation but not their uptake by macrophages. J Nutr. 2003;133:2830–2837. - PubMed
-
- Chao PM, Chao CY, Lin FJ, Huang CJ. Oxidized frying oil up-regulates hepatic acyl-CoA oxidase and cytochrome P450 4A1 genes in rats and activates PPARα. J Nutr. 2001;131:3166–3174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

