Heat shock transcription factor 1 as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 22129991
- PMCID: PMC3518299
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd3453
Heat shock transcription factor 1 as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
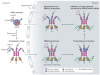
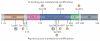
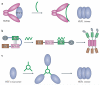
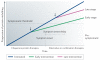
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and prion-based neurodegeneration are associated with the accumulation of misfolded proteins, resulting in neuronal dysfunction and cell death. However, current treatments for these diseases predominantly address disease symptoms, rather than the underlying protein misfolding and cell death, and are not able to halt or reverse the degenerative process. Studies in cell culture, fruitfly, worm and mouse models of protein misfolding-based neurodegenerative diseases indicate that enhancing the protein-folding capacity of cells, via elevated expression of chaperone proteins, has therapeutic potential. Here, we review advances in strategies to harness the power of the natural cellular protein-folding machinery through pharmacological activation of heat shock transcription factor 1--the master activator of chaperone protein gene expression--to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Ross CA, Poirier MA. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nature Med. 2004;10:S10–S17. - PubMed
-
- Haass C, Selkoe DJ. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Muchowski PJ. Protein misfolding, amyloid formation, and neurodegeneration: a critical role for molecular chaperones? Neuron. 2002;35:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Arrasate M, Mitra S, Schweitzer ES, Segal MR, Finkbeiner S. Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature. 2004;431:805–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

