Novel tumor suppressive function of Smad4 in serum starvation-induced cell death through PAK1-PUMA pathway
- PMID: 22130069
- PMCID: PMC3252743
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2011.116
Novel tumor suppressive function of Smad4 in serum starvation-induced cell death through PAK1-PUMA pathway
Abstract
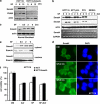
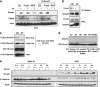
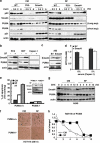
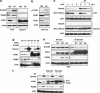
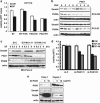
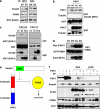
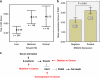
DPC4 (deleted in pancreatic cancer 4)/Smad4 is an essential factor in transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling and is also known as a frequently mutated tumor suppressor gene in human pancreatic and colon cancer. However, considering the fact that TGF-β can contribute to cancer progression through transcriptional target genes, such as Snail, MMPs, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related genes, loss of Smad4 in human cancer would be required for obtaining the TGF-β signaling-independent advantage, which should be essential for cancer cell survival. Here, we provide the evidences about novel role of Smad4, serum-deprivation-induced apoptosis. Elimination of serum can obviously increase the Smad4 expression and induces the cell death by p53-independent PUMA induction. Instead, Smad4-deficient cells show the resistance to serum starvation. Induced Smad4 suppresses the PAK1, which promotes the PUMA destabilization. We also found that Siah-1 and pVHL are involved in PAK1 destabilization and PUMA stabilization. In fact, Smad4-expressed cancer tissues not only show the elevated expression of PAK1, but also support our hypothesis that Smad4 induces PUMA-mediated cell death through PAK1 suppression. Our results strongly suggest that loss of Smad4 renders the resistance to serum-deprivation-induced cell death, which is the TGF-β-independent tumor suppressive role of Smad4.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-cancer effect of novel PAK1 inhibitor via induction of PUMA-mediated cell death and p21-mediated cell cycle arrest.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 4;8(14):23690-23701. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15783. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423593 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β directly induces p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) during the rapid induction of apoptosis in myc-driven B-cell lymphomas.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 15;288(7):5198-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410274. Epub 2012 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23243310 Free PMC article.
-
Par-4 mediated Smad4 induction in PDAC cells restores canonical TGF-β/ Smad4 axis driving the cells towards lethal EMT.Eur J Cell Biol. 2020 May;99(4):151076. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2020.151076. Epub 2020 May 11. Eur J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32439219
-
The role of PRAJA and ELF in TGF-beta signaling and gastric cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2005 Jul;4(7):694-9. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.7.2015. Epub 2005 Jul 13. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16096365 Review.
-
The role of TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling in cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Jan 12;14(2):111-123. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.23230. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29483830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-cancer effect of novel PAK1 inhibitor via induction of PUMA-mediated cell death and p21-mediated cell cycle arrest.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 4;8(14):23690-23701. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15783. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423593 Free PMC article.
-
Combined BCL-2 and PI3K/AKT Pathway Inhibition in KMT2A-Rearranged Acute B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1359. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021359. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674872 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic regulation of oncogenesis by chromatin remodeling.Oncogene. 2016 Aug 25;35(34):4423-36. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.513. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26804164 Review.
-
The impact of TGF-β1 on the mRNA expression of TβR I, TβR II, Smad4 and the invasiveness of the JEG-3 placental choriocarcinoma cell line.Oncol Lett. 2012 Dec;4(6):1344-1348. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.906. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23205135 Free PMC article.
-
Copanlisib promotes growth inhibition and apoptosis by modulating the AKT/FoxO3a/PUMA axis in colorectal cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 2;11(11):943. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03154-w. Cell Death Dis. 2020. Retraction in: Cell Death Dis. 2025 Apr 29;16(1):352. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07679-w. PMID: 33139695 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Weinberg RA. How cancer arises. Sci Am. 1996;275:62–70. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 2004;10:789–799. - PubMed
-
- Bardeesy N, DePinho RA. Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nature Rev Cancer. 2002;2:897–909. - PubMed
-
- Lei M, Lu W, Meng W, Parrini MC, Eck MJ, Mayer BJ, et al. Structure of PAK1 in an autoinhibited conformation reveals a multistage activation switch. Cell. 2000;102:387–397. - PubMed
-
- Hahn SA, Schutte M, Hoque AT, Moskaluk CA, da Costa LT, Rozenblum E, et al. DPC4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome 18q21.1. Science. 1996;271:350–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

