Immunodetection of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is restricted to tissue macrophages in normal rat liver and to recruited mononuclear phagocytes in liver injury and cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 22131058
- PMCID: PMC3262142
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-011-0889-9
Immunodetection of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is restricted to tissue macrophages in normal rat liver and to recruited mononuclear phagocytes in liver injury and cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
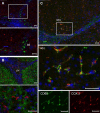
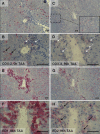
It has been suggested that cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-mediated prostaglandin synthesis is associated with liver inflammation and carcinogenesis. The aim of this study is to identify the cellular source of COX-2 expression in different stages, from acute liver injury through liver fibrosis to cholangiocarcinoma (CC). We induced in rats acute and "chronic" liver injury (thioacetamide (TAA) or carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4))) and CC development (TAA) and assessed COX-2 gene expression in normal and damaged liver tissue by RT-PCR of total RNA. The cellular localization of COX-2 protein in liver tissue was analyzed by immunohistochemistry as well as in isolated rat liver cells by Western blotting. The findings were compared with those obtained in human cirrhotic liver tissue. The specificity of the antibodies was tested by 2-DE Western blot and mass spectrometric identification of the positive protein spots. RT-PCR analysis of total RNA revealed an increase of hepatic COX-2 gene expression in acutely as well as "chronically" damaged liver. COX-2-protein was detected in those ED1(+)/ED2(+) cells located in the non-damaged tissue (resident tissue macrophages). In addition COX-2 positivity in inflammatory mononuclear phagocytes (ED1(+)/ED2(-)), which were also present within the tumoral tissue was detected. COX-2 protein was clearly detectable in isolated Kupffer cells as well as (at lower level) in isolated "inflammatory" macrophages. Similar results were obtained in human cirrhotic liver. COX-2 protein is constitutively detectable in liver tissue macrophages. Inflammatory mononuclear phagocytes contribute to the increase of COX-2 gene expression in acute and chronic liver damage induced by different toxins and in the CC microenvironment.
Figures







Similar articles
-
C1Q synthesis by tissue mononuclear phagocytes from normal and from damaged rat liver: up-regulation by dexamethasone, down-regulation by interferon gamma, and lipopolysaccharide.Hepatology. 1997 Jul;26(1):98-106. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1997.v26.pm0009214457. Hepatology. 1997. PMID: 9214457
-
Emergence of different macrophage populations in hepatic fibrosis following thioacetamide-induced acute hepatocyte injury in rats.J Comp Pathol. 2003 Jan;128(1):41-51. doi: 10.1053/jcpa.2002.0603. J Comp Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12531686
-
Induction of chemokines and cytokines before neutrophils and macrophage recruitment in different regions of rat liver after TAA administration.Lab Invest. 2014 Feb;94(2):235-47. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.134. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Lab Invest. 2014. PMID: 24276236
-
Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases.J Hepatol. 2017 Jun;66(6):1300-1312. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026. Epub 2017 Mar 4. J Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28267621 Review.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
Cited by
-
Fibrosis-associated hepatocarcinogenesis revisited: Establishing standard medium-term chemically-induced male and female models.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 13;13(9):e0203879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203879. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30212575 Free PMC article.
-
The Histochemistry and Cell Biology compendium: a review of 2012.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;139(6):815-46. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1098-5. Epub 2013 May 12. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23665922 Review.
-
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of Boswellia serrate gum resin in CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Feb;19(2):1313-1321. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8353. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32010304 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental origins of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a risk factor for exaggerated metabolic and cardiovascular-renal disease.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):E795-E814. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00394.2017. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29509436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventive effects of combinative natural foods produced by elite crop varieties rich in anticancer effects on N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats.Food Sci Nutr. 2018 Nov 29;7(1):339-355. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.896. eCollection 2019 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30680188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad N, Chen LC, Gordon MA, Laskin JD, Laskin DL. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by nitric oxide in activated hepatic macrophages during acute endotoxemia. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;71:1005–1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

