Dynamic changes in sarcoplasmic reticulum structure in ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 22131804
- PMCID: PMC3206393
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/382586
Dynamic changes in sarcoplasmic reticulum structure in ventricular myocytes
Abstract
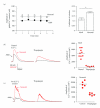
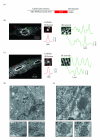
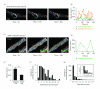
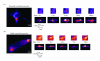
The fidelity of excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in ventricular myocytes is remarkable, with each action potential evoking a [Ca²⁺](i) transient. The prevalent model is that the consistency in EC coupling in ventricular myocytes is due to the formation of fixed, tight junctions between the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and the sarcolemma where Ca²⁺ release is activated. Here, we tested the hypothesis that the SR is a structurally inert organelle in ventricular myocytes. Our data suggest that rather than being static, the SR undergoes frequent dynamic structural changes. SR boutons expressing functional ryanodine receptors moved throughout the cell, approaching or moving away from the sarcolemma of ventricular myocytes. These changes in SR structure occurred in the absence of changes in [Ca²⁺](i) during EC coupling. Microtubules and the molecular motors dynein and kinesin 1(Kif5b) were important regulators of SR motility. These findings support a model in which the SR is a motile organelle capable of molecular motor protein-driven structural changes.
Figures

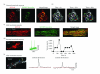
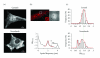
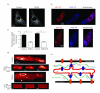
References
-
- Franzini-Armstrong C, Protasi F. Ryanodine receptors of striated muscles: a complex channel capable of multiple interactions. Physiological Reviews. 1997;77(3):699–729. - PubMed
-
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. American journal of physiology. 1983;245(1):C1–C14. - PubMed
-
- Cheng H, Lederer WJ, Cannell MB. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 1993;262(5134):740–744. - PubMed
-
- Gómez AM, Valdivia HH, Cheng H, et al. Defective excitation-contraction coupling in experimental cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Science. 1997;276(5313):800–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

