Thin filament-reconstituted skinned muscle fibers for the study of muscle physiology
- PMID: 22131807
- PMCID: PMC3216491
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/486021
Thin filament-reconstituted skinned muscle fibers for the study of muscle physiology
Abstract
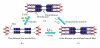
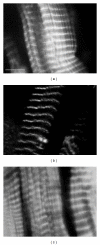
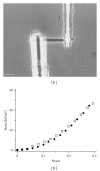
We review the use of thin filament-reconstituted muscle fibers in the study of muscle physiology. Thin filament extraction and reconstitution protocol is a powerful technique to study the role of each component of the thin filament. It is also useful for studying the properties of genetically modified molecules such as actin and tropomyosin. We also review the combination of this protocol with sinusoidal analysis, which will provide a solid technique for determining the effect of regulatory proteins on actomyosin interaction and concomitant cross-bridge kinetics. We suggest that thin filament-reconstituted muscle fibers are an ideal system for studying muscle physiology especially when gene modifications of actin or tropomyosin are involved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Using baculovirus/insect cell expressed recombinant actin to study the molecular pathogenesis of HCM caused by actin mutation A331P.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Sep;74:64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.04.014. Epub 2014 Apr 30. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24793351 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-dependent inhibition of in vitro thin-filament motility by native titin.FEBS Lett. 1996 Feb 19;380(3):281-6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00055-5. FEBS Lett. 1996. PMID: 8601441
-
Elastic behavior of connectin filaments during thick filament movement in activated skeletal muscle.J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2169-76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2169. J Cell Biol. 1989. PMID: 2808523 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of structure and function of sarcomeric actin filaments in striated muscle of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014 Sep;297(9):1548-59. doi: 10.1002/ar.22965. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 25125169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tropomodulin capping of actin filaments in striated muscle development and physiology.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:103069. doi: 10.1155/2011/103069. Epub 2011 Oct 17. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22013379 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Nelutroctiv (CK-136), a Selective Cardiac Troponin Activator for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases Associated with Reduced Cardiac Contractility.J Med Chem. 2024 May 23;67(10):7825-7835. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02413. Epub 2024 May 10. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38729623 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the transcriptomic effects of leucine supplementation on muscle growth and performance in basketball athletes.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0316603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316603. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39854288 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Huxley AF, Niedergerke R. Structural changes in muscle during contraction: interference microscopy of living muscle fibres. Nature. 1954;173(4412):971–973. - PubMed
-
- Huxley H, Hanson J. Changes in the cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their structural interpretation. Nature. 1954;173(4412):973–976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

