Targeted gold nanoparticles enable molecular CT imaging of cancer: an in vivo study
- PMID: 22131831
- PMCID: PMC3224712
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S25446
Targeted gold nanoparticles enable molecular CT imaging of cancer: an in vivo study
Abstract
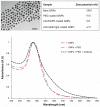
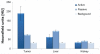
In recent years, advances in molecular biology and cancer research have led to the identification of sensitive and specific biomarkers that associate with various types of cancer. However, in vivo cancer detection methods with computed tomography, based on tracing and detection of these molecular cancer markers, are unavailable today. This paper demonstrates in vivo the feasibility of cancer diagnosis based on molecular markers rather than on anatomical structures, using clinical computed tomography. Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor conjugated gold nanoparticles (30 nm) were intravenously injected into nude mice implanted with human squamous cell carcinoma head and neck cancer. The results clearly demonstrate that a small tumor, which is currently undetectable through anatomical computed tomography, is enhanced and becomes clearly visible by the molecularly-targeted gold nanoparticles. It is further shown that active tumor targeting is more efficient and specific than passive targeting. This noninvasive and nonionizing molecular cancer imaging tool can facilitate early cancer detection and can provide researchers with a new technique to investigate in vivo the expression and activity of cancer-related biomarkers and molecular processes.
Keywords: biologically targeted in vivo imaging; contrast agents; functional computed tomography; gold nanoparticles; molecular imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Branstetter BF, 4th, Blodgett TM, Zimmer LA, et al. Head and neck malignancy: is PET/CT more accurate than PET or CT alone? Radiology. 2005;235(2):580–586. - PubMed
-
- Ross B, Rehemtulla A, Koo YEL, et al. Photonic and magnetic nanoexplorers for biomedical use: from subcellular imaging to cancer diagnostics and therapy. Proceedings of the SPIE – The International Society for Optical Engineering; June 21–25, 2004; Glasgow, Scotland. Bellingham, WA: International Society for Optical Engineering; 2004. pp. 76–83.
-
- Kopelman R, Koo YEL, Philbert M, et al. Multifunctional nanoparticle platforms for in vivo MRI enhancement and photodynamic therapy of a rat brain cancer. J Magn Magn Mater. 2005;293(1):404–410.
-
- Peng C, Wang H, Guo R, et al. Acetylation of dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles: synthesis, stability, and x-ray attenuation properties. J Appl Polym Sci. 2011;119(3):1673–1682.
-
- Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Focella TM, Smilowitz HM. Gold nanoparticles: a new X-ray contrast agent. Br J Radiol. 2006;79(939):248–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

