DNA-PK mediates AKT activation and apoptosis inhibition in clinically acquired platinum resistance
- PMID: 22131882
- PMCID: PMC3223610
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.111032
DNA-PK mediates AKT activation and apoptosis inhibition in clinically acquired platinum resistance
Abstract
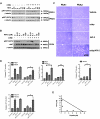
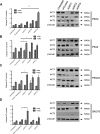
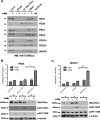
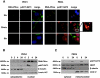
Clinical resistance to chemotherapy is a frequent event in cancer treatment and is closely linked to poor outcome. High-grade serous (HGS) ovarian cancer is characterized by p53 mutation and high levels of genomic instability. Treatment includes platinum-based chemotherapy and initial response rates are high; however, resistance is frequently acquired, at which point treatment options are largely palliative. Recent data indicate that platinum-resistant clones exist within the sensitive primary tumor at presentation, implying resistant cell selection after treatment with platinum chemotherapy. The AKT pathway is central to cell survival and has been implicated in platinum resistance. Here, we show that platinum exposure induces an AKT-dependent, prosurvival, DNA damage response in clinically platinum-resistant but not platinum-sensitive cells. AKT relocates to the nucleus of resistant cells where it is phosphorylated specifically on S473 by DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), and this activation inhibits cisplatin-mediated apoptosis. Inhibition of DNA-PK or AKT, but not mTORC2, restores platinum sensitivity in a panel of clinically resistant HGS ovarian cancer cell lines: we also demonstrate these effects in other tumor types. Resensitization is associated with prevention of AKT-mediated BAD phosphorylation. Strikingly, in patient-matched sensitive cells, we do not see enhanced apoptosis on combining cisplatin with AKT or DNA-PK inhibition. Insulin-mediated activation of AKT is unaffected by DNA-PK inhibitor treatment, suggesting that this effect is restricted to DNA damage-mediated activation of AKT and that, clinically, DNA-PK inhibition might prevent platinum-induced AKT activation without interfering with normal glucose homeostasis, an unwanted toxicity of direct AKT inhibitors.
Figures

References
Supplementary References
-
- Goh LB, Spears KJ, Yao D, Ayrton A, Morgan P, Roland Wolf C, Friedberg T. Endogenous drug transporters in in vitro and in vivo models for the prediction of drug disposition in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64(11):1569–1578. - PubMed
-
- Shahbazi M, Fryer AA, Pravica V, Brogan IJ, Ramsay HM, Hutchinson IV, Harden PN. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms are associated with acute renal allograft rejection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13(1):260–264. - PubMed
References
-
- Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:489–501. - PubMed
-
- Fraser M, Leung BM, Yan X, Dan HC, Cheng JQ, Tsang BK. p53 is a determinant of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein/Akt-mediated chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7081–7088. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Fraser M, Moll UM, Basak A, Tsang BK. Akt-mediated cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer: modulation of p53 action on caspase-dependent mitochondrial death pathway. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3126–3136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
