Management of acute colitis and toxic megacolon
- PMID: 22131898
- PMCID: PMC3134807
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1268254
Management of acute colitis and toxic megacolon
Abstract
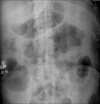
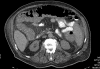
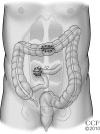
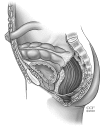
Severe colitis is a well-defined condition that can develop in patients afflicted with ulcerative colitis, but typically responds to a variety of medical therapies. Operative intervention is warranted when massive hemorrhage, perforation, or peritonitis complicates the clinical scenario or medical therapy fails to control the disease. Of the operative options, total/subtotal colectomy and end ileostomy is the usual procedure of choice especially if the operation can be performed through a laparoscopic approach.
Keywords: Ulcerative colitis; acute colitis; ileostomy; total colectomy; toxic colitis.
Figures

References
-
- Silverberg M S, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, et al. Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of inflammatory bowel disease: Report of a Working Party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005;19(Suppl A):5–36. - PubMed
-
- Brown S R, Haboubi N, Hampton J, George B, Travis S PL, ACPGBI The management of acute severe colitis: ACPGBI position statement. Colorectal Dis. 2008;10(Suppl 3):8–29. - PubMed
-
- Kornbluth A, Sachar D B, Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults: American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(3):501–523, quiz 524. - PubMed
-
- Travis S PL, Stange E F, Lémann M, et al. Gassull M for the European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). European evidence-based consensus on the management of ulcerative colitis: current management. J Crohn's Colitis. 2008;2:24–62. - PubMed

