Effect of supplementation with zinc and other micronutrients on malaria in Tanzanian children: a randomised trial
- PMID: 22131908
- PMCID: PMC3222646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001125
Effect of supplementation with zinc and other micronutrients on malaria in Tanzanian children: a randomised trial
Abstract
Background: It is uncertain to what extent oral supplementation with zinc can reduce episodes of malaria in endemic areas. Protection may depend on other nutrients. We measured the effect of supplementation with zinc and other nutrients on malaria rates.
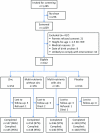
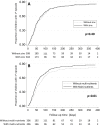
Methods and findings: In a 2×2 factorial trial, 612 rural Tanzanian children aged 6-60 months in an area with intense malaria transmission and with height-for-age z-score≤-1.5 SD were randomized to receive daily oral supplementation with either zinc alone (10 mg), multi-nutrients without zinc, multi-nutrients with zinc, or placebo. Intervention group was indicated by colour code, but neither participants, researchers, nor field staff knew who received what intervention. Those with Plasmodium infection at baseline were treated with artemether-lumefantrine. The primary outcome, an episode of malaria, was assessed among children reported sick at a primary care clinic, and pre-defined as current Plasmodium infection with an inflammatory response, shown by axillary temperature ≥37.5°C or whole blood C-reactive protein concentration ≥ 8 mg/L. Nutritional indicators were assessed at baseline and at 251 days (median; 95% reference range: 191-296 days). In the primary intention-to-treat analysis, we adjusted for pre-specified baseline factors, using Cox regression models that accounted for multiple episodes per child. 592 children completed the study. The primary analysis included 1,572 malaria episodes during 526 child-years of observation (median follow-up: 331 days). Malaria incidence in groups receiving zinc, multi-nutrients without zinc, multi-nutrients with zinc and placebo was 2.89/child-year, 2.95/child-year, 3.26/child-year, and 2.87/child-year, respectively. There was no evidence that multi-nutrients influenced the effect of zinc (or vice versa). Neither zinc nor multi-nutrients influenced malaria rates (marginal analysis; adjusted HR, 95% CI: 1.04, 0.93-1.18 and 1.10, 0.97-1.24 respectively). The prevalence of zinc deficiency (plasma zinc concentration <9.9 µmol/L) was high at baseline (67% overall; 60% in those without inflammation) and strongly reduced by zinc supplementation.
Conclusions: We found no evidence from this trial that zinc supplementation protected against malaria.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00623857
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- IZiNCG. Systematic reviews of zinc intervention strategies. International Zinc Nutrition Consultative Group Technical Document #2. Brown KH, Hess SY, editors. Food Nutr Bull. 2009;30(Suppl.):S1–S184.
-
- Bates CJ, Evans PH, Dardenne M, et al. A trial of zinc supplementation in young rural Gambian children. Br J Nutr. 1993;69:243–255. - PubMed
-
- Shankar AH, Genton B, Baisor M, et al. The influence of zinc supplementation on morbidity due to Plasmodium malaria: a randomized trial in preschool children in Papua New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:663–669. - PubMed
-
- Richard SA, Zavaleta N, Caulfield LE, Black RE, Witzig RS, et al. Zinc and iron supplementation and malaria, diarrhea, and respiratory infections in children in the Peruvian Amazon. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;75:126–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

