Bilingualism and inhibitory control influence statistical learning of novel word forms
- PMID: 22131981
- PMCID: PMC3223905
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00324
Bilingualism and inhibitory control influence statistical learning of novel word forms
Abstract
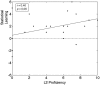
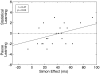
We examined the influence of bilingual experience and inhibitory control on the ability to learn a novel language. Using a statistical learning paradigm, participants learned words in two novel languages that were based on the International Morse Code. First, participants listened to a continuous stream of words in a Morse code language to test their ability to segment words from continuous speech. Since Morse code does not overlap in form with natural languages, interference from known languages was minimized. Next, participants listened to another Morse code language composed of new words that conflicted with the first Morse code language. Interference in this second language was high due to conflict between languages and due to the presence of two colliding cues (compressed pauses between words and statistical regularities) that competed to define word boundaries. Results suggest that bilingual experience can improve word learning when interference from other languages is low, while inhibitory control ability can improve word learning when interference from other languages is high. We conclude that the ability to extract novel words from continuous speech is a skill that is affected both by linguistic factors, such as bilingual experience, and by cognitive abilities, such as inhibitory control.
Keywords: Morse code; Simon task; bilingualism; inhibitory control; language acquisition; statistical learning.
Figures




References
-
- Adesope O. O., Lavin T., Thompson T., Ungerleider C. (2010). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the cognitive correlates of bilingualism. Rev. Educ. Res. 80, 207–245 10.3102/0034654310368803 - DOI
-
- Bartolotti J. V., Marian V. (2010). “Linguistic control in monolingual and bilingual language learners,” in Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society, eds Ohlsson S., Catrambone R. (Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society), 532
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

