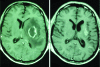
Solitary ring enhancing brain lesion in a patient with AIDS
- PMID: 22132018
- PMCID: PMC3027799
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.09.2009.2237
Solitary ring enhancing brain lesion in a patient with AIDS
Abstract
Toxoplasmosis in immune competent patients usually causes asymptomatic infection or mild symptoms, while in immunocompromised and AIDS patients it can be a life threatening condition. We report a case of cerebral toxoplasmosis in a patient with AIDS and review the causes of brain ring enhancing lesions.
Figures
References
-
- Schroeder PC, Post MJ, Oschatz E, et al. Analysis of the utility of diffusion-weighted MRI and apparent diffusion coefficient values in distinguishing central nervous system toxoplasmosis from lymphoma. Neuroradiology 2006; 48: 715–20 - PubMed
-
- Cunha BA. Central nervous system infections in the compromised host: a diagnostic approach. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2001; 15: 567–90 - PubMed
-
- Rosenow JM, Hirschfeld A. Utility of brain biopsy in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome before and after introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Neurosurgery 2007; 61: 130–41 - PubMed
-
- Antinori A, Larussa D, Cingolani A, et al. Prevalence, associated factors, and prognostic determinants of AIDS-related toxoplasmic encephalitis in the era of advanced highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 1681–91 - PubMed
-
- Katlama C, De Wit S, O’Doherty E, et al. Pyrimethamine-clindamycin vs. pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine as acute and long-term therapy for toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis 1996; 22: 268–75 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources