Mutation of Semaphorin-6A disrupts limbic and cortical connectivity and models neurodevelopmental psychopathology
- PMID: 22132072
- PMCID: PMC3221675
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026488
Mutation of Semaphorin-6A disrupts limbic and cortical connectivity and models neurodevelopmental psychopathology
Abstract
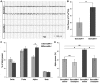
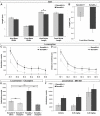
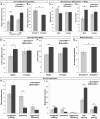
Psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and autism are characterised by cellular disorganisation and dysconnectivity across the brain and can be caused by mutations in genes that control neurodevelopmental processes. To examine how neurodevelopmental defects can affect brain function and behaviour, we have comprehensively investigated the consequences of mutation of one such gene, Semaphorin-6A, on cellular organisation, axonal projection patterns, behaviour and physiology in mice. These analyses reveal a spectrum of widespread but subtle anatomical defects in Sema6A mutants, notably in limbic and cortical cellular organisation, lamination and connectivity. These mutants display concomitant alterations in the electroencephalogram and hyper-exploratory behaviour, which are characteristic of models of psychosis and reversible by the antipsychotic clozapine. They also show altered social interaction and deficits in object recognition and working memory. Mice with mutations in Sema6A or the interacting genes may thus represent a highly informative model for how neurodevelopmental defects can lead to anatomical dysconnectivity, resulting, either directly or through reactive mechanisms, in dysfunction at the level of neuronal networks with associated behavioural phenotypes of relevance to psychiatric disorders. The biological data presented here also make these genes plausible candidates to explain human linkage findings for schizophrenia and autism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
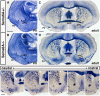
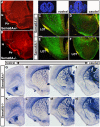
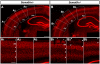
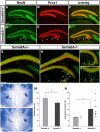
Similar articles
-
Semaphorin-Plexin signaling influences early ventral telencephalic development and thalamocortical axon guidance.Neural Dev. 2017 Apr 24;12(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13064-017-0083-4. Neural Dev. 2017. PMID: 28438183 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 6A knockout mice display abnormalities across ethologically-based topographies of exploration and in motor learning.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Feb 22;641:70-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.01.043. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28109776
-
Sparser and Less Efficient Hippocampal-Prefrontal Projections account for Developmental Network Dysfunction in a Model of Psychiatric Risk Mediated by Gene-Environment Interaction.J Neurosci. 2022 Jan 26;42(4):601-618. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1203-21.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34844990 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological circuits regulating attention, cognitive control, motivation, and emotion: disruptions in neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Apr;51(4):356-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Mar 3. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22449642 Review.
-
[Genetic and pharmacological effects on prefrontal cortical function in schizophrenia].Nervenarzt. 2004 Sep;75(9):845-56. doi: 10.1007/s00115-004-1713-8. Nervenarzt. 2004. PMID: 15372159 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Altered hippocampal-dependent memory and motor function in neuropilin 2-deficient mice.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Mar 3;5(3):e521. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.17. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25734514 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted massively parallel sequencing of autism spectrum disorder-associated genes in a case control cohort reveals rare loss-of-function risk variants.Mol Autism. 2015 Jul 7;6:43. doi: 10.1186/s13229-015-0034-z. eCollection 2015. Mol Autism. 2015. PMID: 26185613 Free PMC article.
-
A novel relationship for schizophrenia, bipolar and major depressive disorder Part 5: a hint from chromosome 5 high density association screen.Am J Transl Res. 2017 May 15;9(5):2473-2491. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28559998 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Study in Sicilian Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 25;12(7):1402. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071402. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061976 Free PMC article.
-
Plexin structures are coming: opportunities for multilevel investigations of semaphorin guidance receptors, their cell signaling mechanisms, and functions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Nov;69(22):3765-805. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1019-0. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22744749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Galaburda AM, LoTurco J, Ramus F, Fitch RH, Rosen GD. From genes to behavior in developmental dyslexia. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1213–1217. - PubMed
-
- Rapoport JL, Addington AM, Frangou S, Psych MR. The neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia: update 2005. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10:434–449. - PubMed
-
- Harrison PJ, Weinberger DR. Schizophrenia genes, gene expression, and neuropathology: on the matter of their convergence. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10:40–68; image 45. - PubMed
-
- Karlsgodt KH, Sun D, Jimenez AM, Lutkenhoff ES, Willhite R, et al. Developmental disruptions in neural connectivity in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Dev Psychopathol. 2008;20:1297–1327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

