Identification and localization of Myxococcus xanthus porins and lipoproteins
- PMID: 22132103
- PMCID: PMC3222651
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027475
Identification and localization of Myxococcus xanthus porins and lipoproteins
Abstract
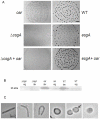
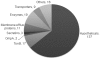
Myxococcus xanthus DK1622 contains inner (IM) and outer membranes (OM) separated by a peptidoglycan layer. Integral membrane, β-barrel proteins are found exclusively in the OM where they form pores allowing the passage of nutrients, waste products and signals. One porin, Oar, is required for intercellular communication of the C-signal. An oar mutant produces CsgA but is unable to ripple or stimulate csgA mutants to develop suggesting that it is the channel for C-signaling. Six prediction programs were evaluated for their ability to identify β-barrel proteins. No program was reliable unless the predicted proteins were first parsed using Signal P, Lipo P and TMHMM, after which TMBETA-SVM and TMBETADISC-RBF identified β-barrel proteins most accurately. 228 β-barrel proteins were predicted from among 7331 protein coding regions, representing 3.1% of total genes. Sucrose density gradients were used to separate vegetative cell IM and OM fractions, and LC-MS/MS of OM proteins identified 54 β-barrel proteins. Another class of membrane proteins, the lipoproteins, are anchored in the membrane via a lipid moiety at the N-terminus. 44 OM proteins identified by LC-MS/MS were predicted lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are distributed between the IM, OM and ECM according to an N-terminal sorting sequence that varies among species. Sequence analysis revealed conservation of alanine at the +7 position of mature ECM lipoproteins, lysine at the +2 position of IM lipoproteins, and no noticable conservation within the OM lipoproteins. Site directed mutagenesis and immuno transmission electron microscopy showed that alanine at the +7 position is essential for sorting of the lipoprotein FibA into the ECM. FibA appears at normal levels in the ECM even when a +2 lysine is added to the signal sequence. These results suggest that ECM proteins have a unique method of secretion. It is now possible to target lipoproteins to specific IM, OM and ECM locations by manipulating the amino acid sequence near the +1 cysteine processing site.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bacterial Outer Membrane Polysaccharide Export (OPX) Proteins Occupy Three Structural Classes with Selective β-Barrel Porin Requirements for Polymer Secretion.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0129022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01290-22. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36200915 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane localization of motility, signaling, and polyketide synthetase proteins in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2003 Sep;185(17):5066-75. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.17.5066-5075.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12923079 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of Outer Membrane Proteins in Treponema denticola by Quantitative Proteome Analyses of Outer Membrane Vesicles and Cellular Fractions.J Proteome Res. 2019 Apr 5;18(4):1567-1581. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00860. Epub 2019 Feb 26. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 30761904
-
Outer membrane lipoprotein biogenesis: Lol is not the end.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Oct 5;370(1679):20150030. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0030. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26370942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secretion of bacterial lipoproteins: through the cytoplasmic membrane, the periplasm and beyond.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1843(8):1509-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.04.022. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24780125 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unmasking of the von Willebrand A-domain surface adhesin CglB at bacterial focal adhesions mediates myxobacterial gliding motility.Sci Adv. 2023 Feb 22;9(8):eabq0619. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq0619. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 36812310 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Outer Membrane Polysaccharide Export (OPX) Proteins Occupy Three Structural Classes with Selective β-Barrel Porin Requirements for Polymer Secretion.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0129022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01290-22. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36200915 Free PMC article.
-
Myxobacterial Genomics and Post-Genomics: A Review of Genome Biology, Genome Sequences and Related 'Omics Studies.Microorganisms. 2021 Oct 13;9(10):2143. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9102143. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34683464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial regulation of the dev operon by MrpC2 and FruA during Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jan;197(2):240-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.02310-14. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25349159 Free PMC article.
-
Myxococcus CsgA, Drosophila Sniffer, and human HSD10 are cardiolipin phospholipases.Genes Dev. 2015 Sep 15;29(18):1903-14. doi: 10.1101/gad.268482.115. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26338420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimkets LJ, Gill RE, Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling during fruiting body development of Myxococcus xanthus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999;53:525–549. - PubMed
-
- Wimley WC. The versatile beta-barrel membrane protein. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13:404–411. - PubMed
-
- Postle K. TonB system, in vivo assays and characterization. Methods Enzymol. 2007;422:245–269. - PubMed
-
- van den Berg B. The FadL family: unusual transporters for unusual substrates. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005;15:401–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

