Structural identifiability of systems biology models: a critical comparison of methods
- PMID: 22132135
- PMCID: PMC3222653
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027755
Structural identifiability of systems biology models: a critical comparison of methods
Abstract
Analysing the properties of a biological system through in silico experimentation requires a satisfactory mathematical representation of the system including accurate values of the model parameters. Fortunately, modern experimental techniques allow obtaining time-series data of appropriate quality which may then be used to estimate unknown parameters. However, in many cases, a subset of those parameters may not be uniquely estimated, independently of the experimental data available or the numerical techniques used for estimation. This lack of identifiability is related to the structure of the model, i.e. the system dynamics plus the observation function. Despite the interest in knowing a priori whether there is any chance of uniquely estimating all model unknown parameters, the structural identifiability analysis for general non-linear dynamic models is still an open question. There is no method amenable to every model, thus at some point we have to face the selection of one of the possibilities. This work presents a critical comparison of the currently available techniques. To this end, we perform the structural identifiability analysis of a collection of biological models. The results reveal that the generating series approach, in combination with identifiability tableaus, offers the most advantageous compromise among range of applicability, computational complexity and information provided.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

 and
and  regard the different generating series coefficients, H is used for zero order coefficients whereas V correspond to the successive Lie derivatives of
regard the different generating series coefficients, H is used for zero order coefficients whereas V correspond to the successive Lie derivatives of  along
along  , for example,
, for example,  . A black square in the coordinates
. A black square in the coordinates  indicates that the corresponding non-zero generating series coefficient
indicates that the corresponding non-zero generating series coefficient  depends on the parameter
depends on the parameter  .
.
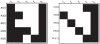
 , regards the
, regards the  component of the
component of the  order coefficients of the Taylor series, (b) Identifiability tableau obtained by means of the generating series method.
order coefficients of the Taylor series, (b) Identifiability tableau obtained by means of the generating series method.
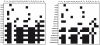

Similar articles
-
Structural Identifiability of Dynamic Systems Biology Models.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Oct 28;12(10):e1005153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005153. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27792726 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic identifiability testing for unambiguous mechanistic modeling--application to JAK-STAT, MAP kinase, and NF-kappaB signaling pathway models.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 May 9;3:50. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-50. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19426527 Free PMC article.
-
Calculating all multiple parameter solutions of ODE models to avoid biological misinterpretations.Math Biosci Eng. 2019 Jul 11;16(6):6438-6453. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2019322. Math Biosci Eng. 2019. PMID: 31698571
-
Review: To be or not to be an identifiable model. Is this a relevant question in animal science modelling?Animal. 2018 Apr;12(4):701-712. doi: 10.1017/S1751731117002774. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Animal. 2018. PMID: 29096725 Review.
-
Inverse Problems in Systems Biology: A Critical Review.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1702:69-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7456-6_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29119503 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous pharmacokinetic model for rolofylline and both M1-trans and M1-cis metabolites.AAPS J. 2013 Apr;15(2):498-504. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9443-5. Epub 2013 Jan 25. AAPS J. 2013. PMID: 23355301 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
ASAS-NANP symposium: Mathematical Modeling in Animal Nutrition: The power of identifiability analysis for dynamic modeling in animal science:a practitioner approach.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad320. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad320. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37997927 Free PMC article.
-
Can Population Modelling Principles be Used to Identify Key PBPK Parameters for Paediatric Clearance Predictions? An Innovative Application of Optimal Design Theory.Pharm Res. 2018 Sep 14;35(11):209. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2487-1. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30218393 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity analysis and inverse uncertainty quantification for the left ventricular passive mechanics.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2022 Jun;21(3):953-982. doi: 10.1007/s10237-022-01571-8. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2022. PMID: 35377030 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying Parameter Interdependence in Stochastic Discrete Models of Biochemical Systems.Entropy (Basel). 2023 Aug 5;25(8):1168. doi: 10.3390/e25081168. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolkenhauer O, Ullah M, Kolch W, Cho K. Modeling and simulation of intracellular dynamics: Choosing an appropriate framework. IEEE Trans on Nanobioscience. 2004;3(3):200–207. - PubMed
-
- Janes K, Lauffenburger D. A biological approach to computational models of proteomic networks. Curr Op Chem Biol. 2006;10:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Banga JR, Balsa-Canto E. Parameter estimation and optimal experimental design. Essays in Biochemistry. 2008;45:195–210. - PubMed
-
- Lipniacki T, Paszek P, Brasier A, Luxon B, Kimmel M. Mathematical model of NFκB regulatory module. J Theor Biol. 2004;228:195–215. - PubMed
-
- Brown K, Hill C, Calero G, Myers C, Lee K, et al. The statistical mechanics of complex signaling networks:nerve growth factor signaling. Phys Biol. 2004;1:184–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

