Novel tools for conservation genomics: comparing two high-throughput approaches for SNP discovery in the transcriptome of the European hake
- PMID: 22132191
- PMCID: PMC3222667
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028008
Novel tools for conservation genomics: comparing two high-throughput approaches for SNP discovery in the transcriptome of the European hake
Abstract
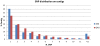
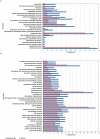
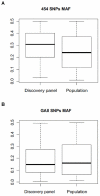
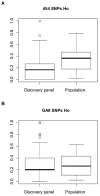
The growing accessibility to genomic resources using next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has revolutionized the application of molecular genetic tools to ecology and evolutionary studies in non-model organisms. Here we present the case study of the European hake (Merluccius merluccius), one of the most important demersal resources of European fisheries. Two sequencing platforms, the Roche 454 FLX (454) and the Illumina Genome Analyzer (GAII), were used for Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) discovery in the hake muscle transcriptome. De novo transcriptome assembly into unique contigs, annotation, and in silico SNP detection were carried out in parallel for 454 and GAII sequence data. High-throughput genotyping using the Illumina GoldenGate assay was performed for validating 1,536 putative SNPs. Validation results were analysed to compare the performances of 454 and GAII methods and to evaluate the role of several variables (e.g. sequencing depth, intron-exon structure, sequence quality and annotation). Despite well-known differences in sequence length and throughput, the two approaches showed similar assay conversion rates (approximately 43%) and percentages of polymorphic loci (67.5% and 63.3% for GAII and 454, respectively). Both NGS platforms therefore demonstrated to be suitable for large scale identification of SNPs in transcribed regions of non-model species, although the lack of a reference genome profoundly affects the genotyping success rate. The overall efficiency, however, can be improved using strict quality and filtering criteria for SNP selection (sequence quality, intron-exon structure, target region score).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
SNP discovery using Next Generation Transcriptomic Sequencing in Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus).PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042089. Epub 2012 Aug 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22879907 Free PMC article.
-
SNP discovery in European anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus, L) by high-throughput transcriptome and genome sequencing.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 1;8(8):e70051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070051. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936375 Free PMC article.
-
Development of high-throughput SNP-based genotyping in Acacia auriculiformis x A. mangium hybrids using short-read transcriptome data.BMC Genomics. 2012 Dec 24;13:726. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-726. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23265623 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in genetics and molecular breeding of three legume crops of semi-arid tropics using next-generation sequencing and high-throughput genotyping technologies.J Biosci. 2012 Nov;37(5):811-20. doi: 10.1007/s12038-012-9228-0. J Biosci. 2012. PMID: 23107917 Review.
-
Role of NGS and SNP genotyping methods in sugarcane improvement programs.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020 Sep;40(6):865-880. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1765730. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32508157 Review.
Cited by
-
EST-Microsatellite Types and Structural Scenarios in European Hake Fisheries.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jun 4;12(11):1462. doi: 10.3390/ani12111462. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681926 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) by 454 deep sequencing: assembly, annotation, and marker discovery.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 23;9(7):e102668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102668. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25054331 Free PMC article.
-
Population-level consequences of complementary sex determination in a solitary parasitoid.BMC Evol Biol. 2015 May 30;15:98. doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0340-2. BMC Evol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26025754 Free PMC article.
-
Whole body transcriptomes and new insights into the biology of the tick Ixodes ricinus.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Jun 26;11(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2932-3. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29941016 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-scale population structure of the northern hard clam (Mercenaria mercenaria) revealed by genome-wide SNP markers.Evol Appl. 2023 Jul 10;16(8):1422-1437. doi: 10.1111/eva.13577. eCollection 2023 Aug. Evol Appl. 2023. PMID: 37622097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oliver P, Massutí E, Alheit J, Pitcher TJ. Biology and fisheries of western Mediterranean hake (M. merluccius). In: Noakes DLG, editor. Hake: Biology, fisheries and markets: Springer Netherlands; 1994. pp. 181–202.
-
- Casey J, Pereiro J, Alheit J, Pitcher TJ. European hake (M. merluccius) in the North-east Atlantic. In: Noakes DLG, editor. Hake: Biology, fisheries and markets: Springer Netherlands; 1994. pp. 125–147.
-
- FAO. FAO yearbook. 2010. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics. 2008.
-
- FAO. 2010. REPORT OF THE 12TH SESSION OF THE SCIENTIFIC ADVISORY COMMITTEE (SAC)-GFCM: XXXIV/2010/Inf.9.
-
- Murua H, Michael L. The Biology and Fisheries of European Hake, Merluccius merluccius, in the North-East Atlantic. 2010. pp. 97–154. Advances in Marine Biology: Academic Press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

