Splicing programs and cancer
- PMID: 22132318
- PMCID: PMC3202119
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/269570
Splicing programs and cancer
Abstract
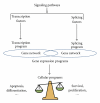
Numerous studies report splicing alterations in a multitude of cancers by using gene-by-gene analysis. However, understanding of the role of alternative splicing in cancer is now reaching a new level, thanks to the use of novel technologies allowing the analysis of splicing at a large-scale level. Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing indicate that splicing alterations can affect the products of gene networks involved in key cellular programs. In addition, many splicing variants identified as being misregulated in cancer are expressed in normal tissues. These observations suggest that splicing programs contribute to specific cellular programs that are altered during cancer initiation and progression. Supporting this model, recent studies have identified splicing factors controlling cancer-associated splicing programs. The characterization of splicing programs and their regulation by splicing factors will allow a better understanding of the genetic mechanisms involved in cancer initiation and progression and the development of new therapeutic targets.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of splicing factors in deregulation of alternative splicing during oncogenesis and tumor progression.Mol Cell Oncol. 2014 Dec 1;2(1):e970955. doi: 10.4161/23723548.2014.970955. eCollection 2015 Jan-Mar. Mol Cell Oncol. 2014. PMID: 27308389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing and tumor progression.Curr Genomics. 2008 Dec;9(8):556-70. doi: 10.2174/138920208786847971. Curr Genomics. 2008. PMID: 19516963 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative transcription and alternative splicing in cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Dec;136(3):283-94. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22909788 Review.
-
The contribution of alternative splicing to genetic risk for psychiatric disorders.Genes Brain Behav. 2018 Mar;17(3):e12430. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12430. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Genes Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 29052934 Review.
-
Entropy measures quantify global splicing disorders in cancer.PLoS Comput Biol. 2008 Mar 14;4(3):e1000011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000011. PLoS Comput Biol. 2008. PMID: 18369415 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aberrant RNA Splicing in Cancer and Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Nov 20;10(11):458. doi: 10.3390/cancers10110458. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30463359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrative framework identifies alternative splicing events in colorectal cancer development.Mol Oncol. 2014 Feb;8(1):129-41. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Oct 19. Mol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24189147 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing within the Wnt signaling pathway: role in cancer development.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016 Feb;39(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s13402-015-0266-0. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016. PMID: 26762488 Review.
-
Identification of recurrent regulated alternative splicing events across human solid tumors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 26;43(10):5130-44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv210. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25908786 Free PMC article.
-
The development and application of small molecule modulators of SF3b as therapeutic agents for cancer.Drug Discov Today. 2013 Jan;18(1-2):43-9. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2012.07.013. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Drug Discov Today. 2013. PMID: 22885522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hallegger M, Llorian M, Smith CWJ. Alternative splicing: global insights: minireview. FEBS Journal. 2010;277(4):856–866. - PubMed
-
- Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nature Genetics. 2008;40(12):1413–1415. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe BJ. Alternative splicing: new insights from global analyses. Cell. 2006;126(1):37–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

