Immunology in the Clinic Review Series; focus on metabolic diseases: development of islet autoimmune disease in type 2 diabetes patients: potential sequelae of chronic inflammation
- PMID: 22132883
- PMCID: PMC3248085
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04501.x
Immunology in the Clinic Review Series; focus on metabolic diseases: development of islet autoimmune disease in type 2 diabetes patients: potential sequelae of chronic inflammation
Abstract
Historically, the development of type 2 diabetes has been considered not to have an autoimmune component, in contrast to the autoimmune pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. In this review we will discuss the accumulating data supporting the concept that islet autoreactivity and inflammation is present in type 2 diabetes pathogenesis, and the islet autoimmunity appears to be one of the factors associated with the progressive nature of the type 2 diabetes disease process.
Published 2011. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures
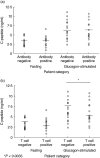
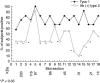
References
-
- Dumitriu IE, Araguas ET, Baboonian C, Kaski JC. CD4+CD28null T cells in coronary artery disease: when helpers become killers. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;81:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Goverman J, Brabb T, Paez A, Harrington C, von Dassow P. Initiation and regulation of CNS autoimmunity. Crit Rev Immunol. 1997;17:469–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

