Proteomics plus genomics approaches in primary immunodeficiency: the case of immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome
- PMID: 22132891
- PMCID: PMC3248093
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04492.x
Proteomics plus genomics approaches in primary immunodeficiency: the case of immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome
Abstract
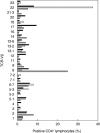
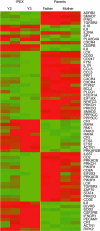
Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) is a rare syndrome due to a mutation in the forkhead box protein 3 gene (FOXP3) leading to an impaired regulatory T cell (T(reg) ) activity associated both with skewed T helper type 2 (Th2) response and autoreactive phenomena. The purpose of this study was to describe a combined proteomics and genomics approach to comprehensively evaluate clinical and immunological phenotypes of patients affected by IPEX. T cell receptor (TCR)-Vβ repertoire and peripheral blood lymphocytes phenotype from three brothers affected by IPEX were studied by flow cytometry. Specific immunoglobulin (Ig)E were evaluated by means of an allergenic molecules microarray [immuno solid-phase allergen chip (ISAC)]. Total RNA was extracted and hybridized to Affymetrix oligonucleotide arrays to obtain quantitative gene-expression levels. No FOXP3 protein was detectable within CD127(-) CD25(high) CD4(+) T cells from peripheral blood. A T cell-naive phenotype (CD62L(+) CD45R0(-)) associated with a reduction of both CD26 and CD7 expression and a TCR-Vβ 8 and 22 family expansions were found. B lymphocytes were mainly CD5(+) (B1) cells expressing a naive phenotype (tcl1(+) CD27(-)). The three IPEX patients had severe food allergy and specific IgE reactivity to cow's milk allergens, a hen's egg allergen and a wheat allergen. Gene expression profile analysis revealed a dysregulation associated mainly with Th1/Th2 pathways. The multiplexing evaluation reported in this study represents a comprehensive approach in the assessment of genetic conditions affecting the immune system such as the IPEX syndrome, paving the way for the development of diagnostic tools to improve the standard clinical and immunological profiling of the disease.
© 2011 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Immunology © 2011 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
References
-
- Baud O, Goulet O, Canioni D, et al. Treatment of the immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1758–62. - PubMed
-
- Gambineri E, Perroni L, Passerini L, et al. Clinical and molecular profile of a new series of patients with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome: Inconsistent correlation between forkhead box protein 3 expression and disease severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:1105–12. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CL, Brunkow ME, Ramsdell F, et al. A rare polyadenylation signal mutation of the FOXP3 gene (AAUAAA–>AAUGAA) leads to the IPEX syndrome. Immunogenetics. 2001;53:435–9. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet. 2001;27:20–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

