Efficacy, safety, and palatability of RACTAB(®) formulation amlodipine orally disintegrating tablets
- PMID: 22133388
- PMCID: PMC3585955
- DOI: 10.2165/11597650-000000000-00000
Efficacy, safety, and palatability of RACTAB(®) formulation amlodipine orally disintegrating tablets
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to confirm the efficacy, safety, and expected palatability of amlodipine orally disintegrating tablets (ODT) [RACTAB(®) formulation (Towa, Osaka, Japan)]. We report the re-analyzed results of 1687 cases in clinical settings obtained through postmarketing surveillance in Japan.
Method: Study subjects were patients receiving treatment for the first time with amlodipine ODT for hypertension under routine care. A multicenter central registration system was used for this prospective survey. The survey was conducted from October 2008 to October 2010. The observational period was 12 weeks, during which time surveys on outpatient blood pressure, adverse events, palatability, etc. were conducted.
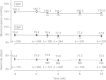
Results: Blood pressure stabilized following treatment, and both systolic and diastolic blood pressures were favorably controlled. Adverse events observed were not significantly different from those observed during drug use trials of amlodipine formulations reported in 2003. Moreover, palatability of amlodipine ODT showed a 99.6% (227 of 228 cases) favorable patient acceptance, which is consistent with the initial design concept of RACTAB(®) formulation.
Conclusions: The results of this postmarketing surveillance study indicated that the efficacy, safety, and palatability of amlodipine ODT met our expectations (dissolves quickly in the mouth, tastes good, and is not rough on the tongue). Accordingly, amlodipine ODT are believed to be an easy-to-use formulation for prescribing doctors, dispensing pharmacists, and patients receiving treatment.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The prediction of the palatability of orally disintegrating tablets by an electronic gustatory system.Int J Pharm. 2015 Sep 30;493(1-2):305-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.07.056. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26216412
-
Evaluation of palatability of 10 commercial amlodipine orally disintegrating tablets by gustatory sensation testing, OD-mate as a new disintegration apparatus and the artificial taste sensor.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;65(9):1312-20. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12101. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23927469
-
Comparative palatability of orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) of Praziquantel (L-PZQ and Rac-PZQ) versus current PZQ tablet in African children: A randomized, single-blind, crossover study.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jun 9;15(6):e0007370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007370. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34106922 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Results of a phase III, 8-week, multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group clinical trial to assess the effects of amlodipine camsylate versus amlodipine besylate in Korean adults with mild to moderate hypertension.Clin Ther. 2007 Sep;29(9):1924-36. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.09.018. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18035192 Clinical Trial.
-
In Vivo Drug Dissolution in Human Oral Cavity from Orally Disintegrating Tablet and Comparability with in Vitro Testing.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2018;66(10):999-1005. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c18-00492. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2018. PMID: 30270246
Cited by
-
Formulations of Amlodipine: A Review.J Pharm (Cairo). 2016;2016:8961621. doi: 10.1155/2016/8961621. Epub 2016 Oct 16. J Pharm (Cairo). 2016. PMID: 27822402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioequivalence of Esaxerenone Conventional Tablet and Orally Disintegrating Tablet: Two Single-Dose Crossover Studies in Healthy Japanese Men.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2022 Aug;11(8):957-965. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.1087. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2022. PMID: 35315257 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ministry of Health, LabourWelfare . Trends in medical care costs. 2011.
-
- Cabinet Office. White paper on aged society: 2010 edition. 2011.
-
- Japan Generic Medicines Association [online; in Japanese]. Available from URL: http://www.jga.gr.jp/medical/generic06.html [Accessed 2011 Jul 1]
-
- Ministry of Health, LabourWelfare. Action programs for promoting safe use of generic medicine: 2007. 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
