Personalized oncology through integrative high-throughput sequencing: a pilot study
- PMID: 22133722
- PMCID: PMC3476478
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003161
Personalized oncology through integrative high-throughput sequencing: a pilot study
Abstract
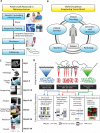
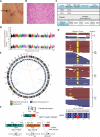
Individual cancers harbor a set of genetic aberrations that can be informative for identifying rational therapies currently available or in clinical trials. We implemented a pilot study to explore the practical challenges of applying high-throughput sequencing in clinical oncology. We enrolled patients with advanced or refractory cancer who were eligible for clinical trials. For each patient, we performed whole-genome sequencing of the tumor, targeted whole-exome sequencing of tumor and normal DNA, and transcriptome sequencing (RNA-Seq) of the tumor to identify potentially informative mutations in a clinically relevant time frame of 3 to 4 weeks. With this approach, we detected several classes of cancer mutations including structural rearrangements, copy number alterations, point mutations, and gene expression alterations. A multidisciplinary Sequencing Tumor Board (STB) deliberated on the clinical interpretation of the sequencing results obtained. We tested our sequencing strategy on human prostate cancer xenografts. Next, we enrolled two patients into the clinical protocol and were able to review the results at our STB within 24 days of biopsy. The first patient had metastatic colorectal cancer in which we identified somatic point mutations in NRAS, TP53, AURKA, FAS, and MYH11, plus amplification and overexpression of cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8). The second patient had malignant melanoma, in which we identified a somatic point mutation in HRAS and a structural rearrangement affecting CDKN2C. The STB identified the CDK8 amplification and Ras mutation as providing a rationale for clinical trials with CDK inhibitors or MEK (mitogen-activated or extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase kinase) and PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) inhibitors, respectively. Integrative high-throughput sequencing of patients with advanced cancer generates a comprehensive, individual mutational landscape to facilitate biomarker-driven clinical trials in oncology.
Figures

References
-
- Meyerson M, Gabriel S, Getz G. Advances in understanding cancer genomes through second-generation sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:685–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

