Overexpression of SET is a recurrent event associated with poor outcome and contributes to protein phosphatase 2A inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 22133779
- PMCID: PMC3347675
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.050542
Overexpression of SET is a recurrent event associated with poor outcome and contributes to protein phosphatase 2A inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: Protein phosphatase 2A is a novel potential therapeutic target in several types of chronic and acute leukemia, and its inhibition is a common event in acute myeloid leukemia. Upregulation of SET is essential to inhibit protein phosphatase 2A in chronic myeloid leukemia, but its importance in acute myeloid leukemia has not yet been explored.
Design and methods: We quantified SET expression by real time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction in 214 acute myeloid leukemia patients at diagnosis. Western blot was performed in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines and in 16 patients' samples. We studied the effect of SET using cell viability assays. Bioinformatics analysis of the SET promoter, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and luciferase assays were performed to evaluate the transcriptional regulation of SET.
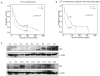
Results: SET overexpression was found in 60/214 patients, for a prevalence of 28%. Patients with SET overexpression had worse overall survival (P<0.01) and event-free survival (P<0.01). Deregulation of SET was confirmed by western blot in both cell lines and patients' samples. Functional analysis showed that SET promotes proliferation, and restores cell viability after protein phosphatase 2A overexpression. We identified EVI1 overexpression as a mechanism involved in SET deregulation in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that SET overexpression is a key mechanism in the inhibition of PP2A in acute myeloid leukemia, and that EVI1 overexpression contributes to the deregulation of SET. Furthermore, SET overexpression is associated with a poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia, and it can be used to identify a subgroup of patients who could benefit from future treatments based on PP2A activators.
Figures
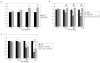


References
-
- Li M, Makkinje A, Damuni Z. The myeloid leukemia-associated protein SET is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(19):11059–62. - PubMed
-
- Seo SB, McNamara P, Heo S, Turner A, Lane WS, Chakravarti D. Regulation of histone acetylation and transcription by INHAT, a human cellular complex containing the set oncoprotein. Cell. 2001;104(1):119–30. - PubMed
-
- Kutney SN, Hong R, Macfarlan T, Chakravarti D. A signaling role of histone-binding proteins and INHAT subunits pp32 and Set/TAF-Ibeta in integrating chromatin hypoacetylation and transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(29):30850–5. - PubMed
-
- Kandilci A, Mientjes E, Grosveld G. Effects of SET and SET-CAN on the differentiation of the human promonocytic cell line U937. Leukemia. 2004;18(2):337–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

