Thrombolytic therapy is effective in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: a series of nine patients and a review of the literature
- PMID: 22133780
- PMCID: PMC3291587
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.049767
Thrombolytic therapy is effective in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: a series of nine patients and a review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Thrombosis is the major risk factor for death in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Previous case reports indicate that venous thrombosis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is amenable to thrombolysis.
Design and methods: We reviewed the outcome of thrombolytic therapy for patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria who had thromboses refractory to anticoagulation at our institutions.
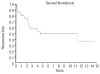
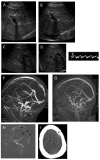
Results: In this study of 41 patients who had at least one thrombotic event, we confirmed a very high incidence of recurrence despite anticoagulation. Nine patients with thrombosis were regarded as eligible for administration of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator, which was effective in reversing thrombi in all of 15 occasions in which it was given. Serious hemorrhagic complications developed in three cases. At last follow-up visit, of the nine patients treated, three had died, and six were in very good to excellent condition in terms of clinical outcome and radiological findings. The only patient in whom thrombolysis may have contributed to a fatal outcome also had complications of "heparin induced thrombocytopenia with thrombosis", which we diagnosed in three additional patients. In our review of the literature, nine out of 15 patients treated with thrombolysis have had a good outcome.
Conclusions: Although it is associated with a significant but manageable risk of bleeding, systemic thrombolysis is a highly effective treatment for reversing venous thromboses in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Figures
References
-
- Araten D, Thaler H, Luzzatto L. High incidence of thrombosis in African-American and Latin-American patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93(1):88–91. - PubMed
-
- Hall C, Richards S, Hillmen P. Primary pro-phylaxis with warfarin prevents thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) Blood. 2003;102(10):3587–91. - PubMed
-
- Hillmen P, Lewis S, Bessler M, Luzzatto L, Dacie J. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(19):1253–8. - PubMed
-
- Socie G, Mary J, deGramont A, Rio B, Leporrier M, Rose C, et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: long-term follow-up and prognostic factors. Lancet. 1996;348(9027):573–7. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura J, Kanakura Y, Ware R, Shichishima T, Nakakuma H, Ninomiya H, et al. Clinical course and flow cytometric analysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in the United States and Japan. Medicine (Baltimore) 2004;83(3):193–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

