Vaginal microbiome and sexually transmitted infections: an epidemiologic perspective
- PMID: 22133886
- PMCID: PMC3225992
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI57172
Vaginal microbiome and sexually transmitted infections: an epidemiologic perspective
Abstract
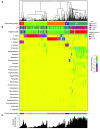
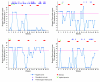
Vaginal bacterial communities are thought to help prevent sexually transmitted infections. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common clinical syndrome in which the protective lactic acid-producing bacteria (mainly species of the Lactobacillus genus) are supplanted by a diverse array of anaerobic bacteria. Epidemiologically, BV has been shown to be an independent risk factor for adverse outcomes including preterm birth, development of pelvic inflammatory disease, and acquisition of sexually transmitted infections. Longitudinal studies of the vaginal microbiome using molecular techniques such as 16S ribosomal DNA analysis may lead to interventions that shift the vaginal microbiota toward more protective states.
Figures
References
-
- Hillier SL, Holmes KK, Marrazzo JM. Bacterial vaginosis. In: Holmes K, et al.Sexually Transmitted Diseases . New York New York, USA: McGraw–Hill, Health Professions Division; 2008:737–768.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

