Realgar-induced apoptosis and differentiation in all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-sensitive NB4 and ATRA-resistant MR2 cells
- PMID: 22134377
- PMCID: PMC3584620
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1276
Realgar-induced apoptosis and differentiation in all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-sensitive NB4 and ATRA-resistant MR2 cells
Abstract
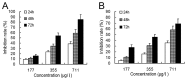
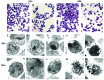
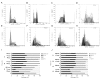
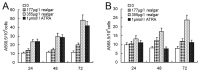
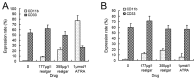
Realgar has been used in Western medicine and Chinese traditional medicine since ancient times, and its promising anticancer activity has attracted much attention in recent years, especially for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). However, the therapeutic action of realgar treatment for APL remains to be fully elucidated. Cellular cytotoxicity, proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation were comprehensively investigated in realgar-treated cell lines derived from PML-RARα+ APL patient, including the all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-sensitive NB4 and ATRA-resistant MR2 cell lines. For analysis of key regulators of apoptosis and differentiation, gene expression profiles were performed in NB4 cells. Realgar was found to induce apoptosis and differentiation in both cell lines, and these effects were exerted simultaneously. Gene expression profiles indicated that genes influenced by realgar treatment were involved in the modulation of signal transduction, translation, transcription, metabolism and the immune response. Given its low toxicity, realgar is a promising alternative reagent for the therapy of APL. Our data contribute to an understanding of the underlying mechanism responsible for the therapeutic effects of realgar in the clinical treatment of APL.
Figures
References
-
- Cunningham I, Gee TS, Reich LM, Kempin SJ, Naval AN, Clarkson BD. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: treatment results during a decade at Memorial Hospital. Blood. 1989;73:1116–1122. - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro RC, Rego E. Management of APL in developing countries: epidemiology, challenges and opportunities for international collaboration. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Sanz MA, Jarque I, Martin G, et al. Acute promyelocytic leukemia. Therapy results and prognostic factors. Cancer. 1988;61:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZY, Chen Z. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: from highly fatal to highly curable. Blood. 2008;111:2505–2515. - PubMed
-
- Niu C, Yan H, Yu T, et al. Studies on treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide: remission induction, follow-up, and molecular monitoring in 11 newly diagnosed and 47 relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia patients. Blood. 1999;94:3315–3324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

