Glucocorticoids and relapse and infection rates in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody disease
- PMID: 22134625
- PMCID: PMC3280023
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05610611
Glucocorticoids and relapse and infection rates in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: The optimal course of glucocorticoid therapy in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA) disease is unknown. This cohort study evaluates effects of glucocorticoid therapy duration on patient outcomes and adverse events.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This study assessed 147 patients diagnosed between January 1, 2000 and January 1, 2009 who were treated with glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide. Patients with end stage kidney disease at presentation, treatment resistance, or who had died within 6 months were excluded. Patients were divided into three groups: 0, 5, or >5 mg prednisone daily at 6 months after therapy initiation. The latter two groups were combined for assessment of adverse events. Wilcoxon rank sum, Kruskal-Wallis, or Fisher's exact tests were used for between-group comparisons. Time to relapse was evaluated by the Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test for comparison.
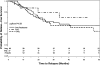
Results: There were no differences between groups in ANCA specificity, serum creatinine, frequency of risk factors for relapse, or length of therapy with immunosuppressants. Length of glucocorticoid therapy had no impact on time to relapse (hazard ratio, 0.69 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.23-2.02]; 1.01, [95% CI, 0.57-1.81] for the 5-mg and >5-mg groups, respectively), relapse-free survival, end stage kidney disease, or death. Patients receiving glucocorticoids beyond 6 months had significantly higher incidence of infections (0.64 infections per person-year versus 0.39, P<0.0001) and a marginally significant higher frequency of new-onset diabetes mellitus (odds ratio, 2.03; 95% CI, 0.94-4.38).
Conclusions: Glucocorticoid therapy beyond 6 months is associated with a significantly greater risk of infections but not a significantly decreased risk of relapse.
Figures
References
-
- Fauci AS, Wolff SM, Johnson JS: Effect of cyclophosphamide upon the immune response in Wegener’s granulomatosis. N Engl J Med 285: 1493–1496, 1971 - PubMed
-
- Novack SN, Pearson CM: Cyclophosphamide therapy in Wegener’s granulomatosis. N Engl J Med 284: 938–942, 1971 - PubMed
-
- Nachman PH, Hogan SL, Jennette JC, Falk RJ: Treatment response and relapse in antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated microscopic polyangiitis and glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 33–39, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Holle JU, Gross WL, Latza U, Nölle B, Ambrosch P, Heller M, Fertmann R, Reinhold-Keller E: Improved outcome in 445 patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis in a German vasculitis center over four decades. Arthritis Rheum 63: 257–266, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Hogan SL, Falk RJ, Chin H, Cai J, Jennette CE, Jennette JC, Nachman PH: Predictors of relapse and treatment resistance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated small-vessel vasculitis. Ann Intern Med 143: 621–631, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical