Acute running stimulates hippocampal dopaminergic neurotransmission in rats, but has no influence on brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 22134693
- PMCID: PMC3289437
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00306.2011
Acute running stimulates hippocampal dopaminergic neurotransmission in rats, but has no influence on brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
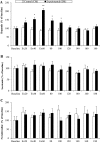
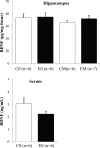
Hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein is increased with exercise in rats. Monoamines seem to play a role in the regulation of BDNF, and monoamine neurotransmission is known to increase with exercise. The purpose of this study was to examine the influence of acute exercise on monoaminergic neurotransmission and BDNF protein concentrations. Hippocampal microdialysis was performed in rats that were subjected to 60 min of treadmill running at 20 m/min or rest. Two hours postexercise, the rats were killed, and the hippocampus was dissected. In experiments without microdialysis, hippocampus and serum samples were collected immediately after exercise. Exercise induced a twofold increase in hippocampal dopamine release. Noradrenaline and serotonin release were not affected. Hippocampal BDNF levels were not influenced, whether they were measured immediately or 2 h after the exercise protocol. Serum BDNF levels did not change either, but serum BDNF was negatively correlated to peripheral corticosterone concentrations, indicating a possible inhibitory reaction to the stress of running. Sixty minutes of exercise enhances dopamine release in the hippocampus of the rat in vivo. However, this increase is not associated with changes in BDNF protein levels immediately nor 2 h after the acute exercise bout. An increased corticosterone level might be the contributing factor for the absence of changes in BDNF.
Figures


References
-
- Angelucci F, Brenè S, Mathé AA. BDNF in schizophrenia, depression and corresponding animal models. Mol Psychiatry 10: 345–352, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Berchtold NC, Chinn G, Chou M, Kesslak JP, Cotman CW. Exercise primes a molecular memory for brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein induction in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 133: 853–861, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Chaouloff F, Laude D, Merino D, Serrurrier B, Guezennec Y, Elghozi J. Amphetamine and alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine affect the exercise-induced imbalance between the availability of tryptophan and synthesis of serotonin in the brain of the rat. Neuropharmacology 26: 1099–1106, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Chen MJ, Nguyen TV, Pike CJ, Russo-Neustadt AA. Norepinephrine induces BDNF and activates the PI-3K and MAPK cascades in embryonic hippocampal neurons. Cell Signal 19: 114–128, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cotman CW, Berchtold NC. Exercise: a behavioral intervention to enhance brain health and plasticity. Trends Neurosci 25: 295–301, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

