Post hoc immunostaining of GABAergic neuronal subtypes following in vivo two-photon calcium imaging in mouse neocortex
- PMID: 22134770
- PMCID: PMC3261390
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-011-1048-9
Post hoc immunostaining of GABAergic neuronal subtypes following in vivo two-photon calcium imaging in mouse neocortex
Abstract
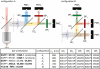
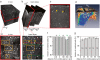
GABAergic neurons in the neocortex are diverse with regard to morphology, physiology, and axonal targeting pattern, indicating functional specializations within the cortical microcircuitry. Little information is available, however, about functional properties of distinct subtypes of GABAergic neurons in the intact brain. Here, we combined in vivo two-photon calcium imaging in supragranular layers of the mouse neocortex with post hoc immunohistochemistry against the three calcium-binding proteins parvalbumin, calretinin, and calbindin in order to assign subtype marker profiles to neuronal activity. Following coronal sectioning of fixed brains, we matched cells in corresponding volumes of image stacks acquired in vivo and in fixed brain slices. In GAD67-GFP mice, more than 95% of the GABAergic cells could be unambiguously matched, even in large volumes comprising more than a thousand interneurons. Triple immunostaining revealed a depth-dependent distribution of interneuron subtypes with increasing abundance of PV-positive neurons with depth. Most importantly, the triple-labeling approach was compatible with previous in vivo calcium imaging following bulk loading of Oregon Green 488 BAPTA-1, which allowed us to classify spontaneous calcium transients recorded in vivo according to the neurochemically defined GABAergic subtypes. Moreover, we demonstrate that post hoc immunostaining can also be applied to wild-type mice expressing the genetically encoded calcium indicator Yellow Cameleon 3.60 in cortical neurons. Our approach is a general and flexible method to distinguish GABAergic subtypes in cell populations previously imaged in the living animal. It should thus facilitate dissecting the functional roles of these subtypes in neural circuitry.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Preprodynorphin-expressing neurons constitute a large subgroup of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic interneurons in the mouse neocortex.J Comp Neurol. 2014 May 1;522(7):1506-26. doi: 10.1002/cne.23477. J Comp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24122731
-
Postnatal development of GABAergic interneurons in the neocortical subplate of mice.Neuroscience. 2016 May 13;322:78-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.023. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26892297
-
Density and neurochemical profiles of neuronal nitric oxide synthase-expressing interneuron in the mouse basolateral amygdala.Brain Res. 2017 May 15;1663:106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28213154
-
Cellular distribution of the calcium-binding proteins parvalbumin, calbindin, and calretinin in the neocortex of mammals: phylogenetic and developmental patterns.J Chem Neuroanat. 1999 Feb;16(2):77-116. doi: 10.1016/s0891-0618(98)00065-9. J Chem Neuroanat. 1999. PMID: 10223310 Review.
-
Cortical interneuron fate determination: diverse sources for distinct subtypes?Cereb Cortex. 2003 Jun;13(6):670-6. doi: 10.1093/cercor/13.6.670. Cereb Cortex. 2003. PMID: 12764043 Review.
Cited by
-
Light-guided sectioning for precise in situ localization and tissue interface analysis for brain-implanted optical fibers and GRIN lenses.Cell Rep. 2021 Sep 28;36(13):109744. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109744. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34592157 Free PMC article.
-
Finding a Needle in a Haystack: Identification of EGFP Tagged Neurons during Calcium Imaging by Means of Two-Photon Spectral Separation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Oct 29;5:96. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00096. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23112759 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale 3D Two-Photon Imaging of Molecularly Identified CA1 Interneuron Dynamics in Behaving Mice.Neuron. 2020 Dec 9;108(5):968-983.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.09.013. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 33022227 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging neuronal populations in behaving rodents: paradigms for studying neural circuits underlying behavior in the mammalian cortex.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 6;33(45):17631-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3255-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24198355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-yield in vitro recordings from neurons functionally characterized in vivo.Nat Protoc. 2018 Jun;13(6):1275-1293. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2018.026. Epub 2018 May 10. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29748648
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophot Int. 2004;11(7):36–42.
-
- Ascoli GA, Alonso-Nanclares L, Anderson SA, Barrionuevo G, Benavides-Piccione R, Burkhalter A, Buzsáki G, Cauli B, Defelipe J, Fairén A, Feldmeyer D, Fishell G, Fregnac Y, Freund TF, Gardner D, Gardner EP, Goldberg JH, Helmstaedter M, Hestrin S, Karube F, Kisvárday ZF, Lambolez B, Lewis DA, Marin O, Markram H, Muñoz A, Packer A, Petersen CC, Rockland KS, Rossier J, Rudy B, Somogyi P, Staiger JF, Tamas G, Thomson AM, Toledo-Rodriguez M, Wang Y, West DC, Yuste R. Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9(7):557–568. doi: 10.1038/nrn2402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

