Effects of alfalfa and organic fertilizer on benzo[a]pyrene dissipation in an aged contaminated soil
- PMID: 22134861
- PMCID: PMC3386484
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-011-0672-4
Effects of alfalfa and organic fertilizer on benzo[a]pyrene dissipation in an aged contaminated soil
Abstract
Background: A climate-controlled pot experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of planting alfalfa and applying organic fertilizer on the dissipation of benzo[a]pyrene from an aged contaminated agricultural soil.
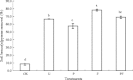
Results: Short-term planting of alfalfa inhibited the dissipation of benzo[a]pyrene from the soil by 8.9%, and organic fertilizer enhanced benzo[a]pyrene removal from the soil by 11.6% compared with the unplanted and unfertilized treatments, respectively. No significant interaction was observed between alfalfa and organic fertilizer on benzo[a]pyrene dissipation. Sterilization completely inhibited the removal of benzo[a]pyrene from the soil indicating that its degradation by indigenous microorganisms may have been the main mechanism of dissipation. Furthermore, significant positive relationships were observed between benzo[a]pyrene removal and the contents of soil ammonium nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, and total mineral nitrogen at the end of the experiment, suggesting that competition between plants and microorganisms for nitrogen may have inhibited benzo[a]pyrene dissipation in the rhizosphere of alfalfa and the addition of organic fertilizer may facilitate microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene in the soil.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promotion of pyrene degradation in rhizosphere of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.).Chemosphere. 2008 Apr;71(8):1593-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.068. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Chemosphere. 2008. PMID: 18082869
-
Phytoremediation of pyrene contaminated soils amended with compost and planted with ryegrass and alfalfa.Chemosphere. 2012 Apr;87(3):217-25. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.063. Epub 2012 Jan 14. Chemosphere. 2012. PMID: 22245074
-
Uptake and translocation of benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) in two ornamental plants and dissipation in soil.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016 Feb;124:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.09.037. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016. PMID: 26476328
-
[Study on phytoremediation of phenanthrene-contaminated soil with alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2007 Sep;28(9):2080-4. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2007. PMID: 17990561 Chinese.
-
Degradation of benzo[a]pyrene in soil with arbuscular mycorrhizal alfalfa.Environ Geochem Health. 2004 Jun-Sep;26(2-3):285-93. doi: 10.1023/b:egah.0000039592.80489.e5. Environ Geochem Health. 2004. PMID: 15499785
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Different Nutritional and Environmental Parameters on Microbial Pyrene Degradation by Mangrove Culturable Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 5;24(9):8282. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098282. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175988 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of single and mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination on plant biomass yield and PAH dissipation during phytoremediation.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Jul;25(19):18596-18603. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1987-1. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29704177 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-bacteria partnerships for the remediation of persistent organic pollutants.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Feb;24(5):4322-4336. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4935-3. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 26139403
References
-
- Binet P, Portal JM, Leyval C. Dissipation of 3–6-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rhizosphere of ryegrass. Soil Biol Biochem. 2000;32:2011–2017. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00100-0. - DOI
-
- Bossert ID, Bartha R (1986) Structure-biodegradability relationships of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. B Environ Contam Tox 37:490–495 - PubMed
-
- CCME . Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health: summary tables. Updated. Winnipeg: CCME; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources