Imaging approaches for dementia
- PMID: 22135130
- PMCID: PMC7964608
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2782
Imaging approaches for dementia
Abstract
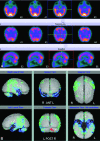
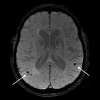
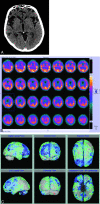
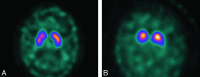
Brain imaging has progressed from exclusion of rare treatable mass lesions to a specific antemortem diagnosis. MR imaging-derived hippocampal atrophy and WMH are regarded as imaging biomarkers of AD and CVD respectively. Abnormal FP-CIT SPECT or cardiac iodobenzamide SPECT is a useful supportive imaging feature in the diagnosis of DLB. Frontal and/or anterior temporal atrophy and anterior defects on molecular imaging with FDG-PET or perfusion SPECT are characteristic of FTDs. Whole-body FDG-PET may be helpful in patients with rapidly progressing "autoimmune dementias," and FLAIR and DWI are indicated in suspected CJD. A major role of imaging is in the development of new drugs and less costly biomarkers.
Figures




References
-
- Knopman DS, DeKosky ST, Cummings JL, et al. . Practice parameter: diagnosis of dementia (an evidence-based review. Report of the quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology). Neurology 2001;56:1143–53 - PubMed
-
- Matsuda H. Role of neuroimaging in Alzheimer's disease, with emphasis on brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1289–300 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
