Direct analysis and identification of pathogenic Lichtheimia species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight analyzer-mediated mass spectrometry
- PMID: 22135259
- PMCID: PMC3264171
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01070-11
Direct analysis and identification of pathogenic Lichtheimia species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight analyzer-mediated mass spectrometry
Abstract
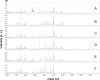
Zygomycetes of the order Mucorales can cause life-threatening infections in humans. These mucormycoses are emerging and associated with a rapid tissue destruction and high mortality. The resistance of Mucorales to antimycotic substances varies between and within clinically important genera such as Mucor, Rhizopus, and Lichtheimia. Thus, an accurate diagnosis before onset of antimycotic therapy is recommended. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI)-time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometry (MS) is a potentially powerful tool to rapidly identify infectious agents on the species level. We investigated the potential of MALDI-TOF MS to differentiate Lichtheimia species, one of the most important agents of mucormycoses. Using the Bruker Daltonics FlexAnalysis (version 3.0) software package, a spectral database library with m/z ratios of 2,000 to 20,000 Da was created for 19 type and reference strains of clinically relevant Zygomycetes of the order Mucorales (12 species in 7 genera). The database was tested for accuracy by use of 34 clinical and environmental isolates of Lichtheimia comprising a total of five species. Our data demonstrate that MALDI-TOF MS can be used to clearly discriminate Lichtheimia species from other pathogenic species of the Mucorales. Furthermore, the method is suitable to discriminate species within the genus. The reliability and robustness of the MALDI-TOF-based identification are evidenced by high score values (above 2.3) for the designation to a certain species and by moderate score values (below 2.0) for the discrimination between clinically relevant (Lichtheimia corymbifera, L. ramosa, and L. ornata) and irrelevant (L. hyalospora and L. sphaerocystis) species. In total, all 34 strains were unequivocally identified by MALDI-TOF MS with score values of >1.8 down to the generic level, 32 out of 34 of the Lichtheimia isolates (except CNM-CM 5399 and FSU 10566) were identified accurately with score values of >2 (probable species identification), and 25 of 34 isolates were identified to the species level with score values of >2.3 (highly probable species identification). The MALDI-TOF MS-based method reported here was found to be reproducible and accurate, with low consumable costs and minimal preparation time.
Figures


References
-
- Alanio A, et al. 2011. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for fast and accurate identification of clinically relevant Aspergillus species. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 17: 750–755 - PubMed
-
- Alastruey-Izquierdo A, et al. 2009. In vitro activity of antifungals against Zygomycetes. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 15 Suppl 5: 71–76 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

