Structural complex of sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) with 14α-methylenecyclopropyl-Delta7-24, 25-dihydrolanosterol
- PMID: 22135275
- PMCID: PMC3269163
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M021865
Structural complex of sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) with 14α-methylenecyclopropyl-Delta7-24, 25-dihydrolanosterol
Abstract
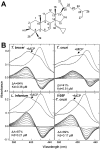
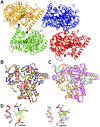
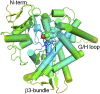
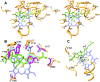
Sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) that catalyzes the removal of the 14α-methyl group from the sterol nucleus is an essential enzyme in sterol biosynthesis, a primary target for clinical and agricultural antifungal azoles and an emerging target for antitrypanosomal chemotherapy. Here, we present the crystal structure of Trypanosoma (T) brucei CYP51 in complex with the substrate analog 14α-methylenecyclopropyl-Δ7-24,25-dihydrolanosterol (MCP). This sterol binds tightly to all protozoan CYP51s and acts as a competitive inhibitor of F105-containing (plant-like) T. brucei and Leishmania (L) infantum orthologs, but it has a much stronger, mechanism-based inhibitory effect on I105-containing (animal/fungi-like) T. cruzi CYP51. Depicting substrate orientation in the conserved CYP51 binding cavity, the complex specifies the roles of the contact amino acid residues and sheds new light on CYP51 substrate specificity. It also provides an explanation for the effect of MCP on T. cruzi CYP51. Comparison with the ligand-free and azole-bound structures supports the notion of structural rigidity as the characteristic feature of the CYP51 substrate binding cavity, confirming the enzyme as an excellent candidate for structure-directed design of new drugs, including mechanism-based substrate analog inhibitors.
Figures
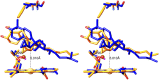
References
-
- Nes W. R., McKean M. R., 1977. Biochemistry of Steroids and Other Isopentenoids. University Park Press, Baltimore.
-
- Bloch K. E. 1983. Sterol structure and membrane function. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 14: 47–92. - PubMed
-
- Volkman J. K. 2005. Sterols and other triterpenoids: source specificity and evolution of biosynthetic pathways. Org. Geochem. 36: 139–159.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

