Sodium intake, ACE inhibition, and progression to ESRD
- PMID: 22135311
- PMCID: PMC3269916
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011040430
Sodium intake, ACE inhibition, and progression to ESRD
Abstract
High sodium intake limits the antihypertensive and antiproteinuric effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors in patients with CKD; however, whether dietary sodium also associates with progression to ESRD is unknown. We conducted a post hoc analysis of the first and second Ramipril Efficacy in Nephropathy trials to evaluate the association of sodium intake with proteinuria and progression to ESRD among 500 CKD patients without diabetes who were treated with ramipril (5 mg/d) and monitored with serial 24-hour urinary sodium and creatinine measurements. Urinary sodium/creatinine excretion defined low (<100 mEq/g), medium (100 to <200 mEq/g), and high (≥200 mEq/g) sodium intake. During a follow-up of >4.25 years, 92 individuals (18.4%) developed ESRD. Among those with low, medium, and high sodium intakes, the incidence of ESRD was 6.1 (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 3.8-9.7), 7.9 (95% CI, 6.1-10.2), and 18.2 (95% CI, 11.3-29.3) per 100 patient-years, respectively (P<0.001). Patients with high dietary sodium exhibited a blunted antiproteinuric effect of ACE inhibition despite similar BP among groups. Each 100-mEq/g increase in urinary sodium/creatinine excretion associated with a 1.61-fold (95% CI, 1.15-2.24) higher risk for ESRD; adjusting for baseline proteinuria attenuated this association to 1.38-fold (95% CI, 0.95-2.00). This association was independent from BP but was lost after adjusting for changes in proteinuria. In summary, among patients with CKD but without diabetes, high dietary salt (>14 g daily) seems to blunt the antiproteinuric effect of ACE inhibitor therapy and increase the risk for ESRD, independent of BP control.
Figures
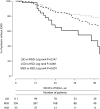


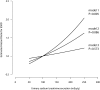
Comment in
-
Sodium intake, ACE inhibition, and progression to ESRD.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jan;23(1):10-2. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011111107. Epub 2011 Dec 15. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22173698 No abstract available.
-
Progression of renal disease: High salt intake blunts the benefit of ACE inhibitors and accelerates renal function decline.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012 Jan 10;8(2):61. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.198. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22231133 No abstract available.
References
-
- The GISEN Group (Gruppo Italiano di Studi Epidemiologici in Nefrologia): Randomised placebo-controlled trial of effect of ramipril on decline in glomerular filtration rate and risk of terminal renal failure in proteinuric, non-diabetic nephropathy. Lancet 349: 1857–1863, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Gherardi G, Garini G, Zoccali C, Salvadori M, Scolari F, Schena FP, Remuzzi G: Renoprotective properties of ACE-inhibition in non-diabetic nephropathies with non-nephrotic proteinuria. Lancet 354: 359–364, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Gherardi G, Gaspari F, Benini R, Remuzzi G: Renal function and requirement for dialysis in chronic nephropathy patients on long-term ramipril: REIN follow-up trial. Gruppo Italiano di Studi Epidemiologici in Nefrologia (GISEN). Ramipril Efficacy in Nephropathy. Lancet 352: 1252–1256, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Remuzzi G. GISEN Group Investigators: Retarding progression of chronic renal disease: The neglected issue of residual proteinuria. Kidney Int 63: 2254–2261, 2003 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

