Novel transcript truncating function of Rap1p revealed by synthetic codon-optimized Ty1 retrotransposon
- PMID: 22135353
- PMCID: PMC3276619
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.111.136648
Novel transcript truncating function of Rap1p revealed by synthetic codon-optimized Ty1 retrotransposon
Abstract
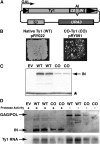
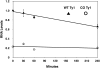
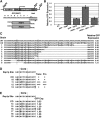
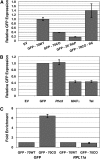
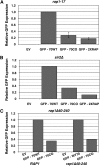
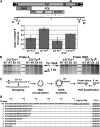
Extensive mutagenesis via massive recoding of retrotransposon Ty1 produced a synthetic codon-optimized retrotransposon (CO-Ty1). CO-Ty1 is defective for retrotransposition, suggesting a sequence capable of down-regulating retrotransposition. We mapped this sequence to a critical ~20-bp region within CO-Ty1 reverse transcriptase (RT) and confirmed that it reduced Ty1 transposition, protein, and RNA levels. Repression was not Ty1 specific; when introduced immediately downstream of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) stop codon, GFP expression was similarly reduced. Rap1p mediated this down-regulation, as shown by mutagenesis and chromatin immunoprecipitation. A regular threefold drop is observed in different contexts, suggesting utility for synthetic circuits. A large reduction of RNAP II occupancy on the CO-Ty1 construct was observed 3' to the identified Rap1p site and a novel 3' truncated RNA species was observed. We propose a novel mechanism of transcriptional regulation by Rap1p whereby it serves as a transcriptional roadblock when bound to transcription unit sequences.
Figures

References
-
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R., 1987. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 154: 164–175 - PubMed
-
- Braiterman L. T., Monokian G. M., Eichinger D. J., Merbs S. L., Gabriel A., et al. , 1994. In-frame linker insertion mutagenesis of yeast transposon Ty1: phenotypic analysis. Gene 139: 19–26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

