Intercellular protein movement in syncytial Drosophila follicle cells
- PMID: 22135360
- PMCID: PMC3244987
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.090456
Intercellular protein movement in syncytial Drosophila follicle cells
Abstract
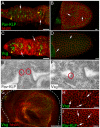
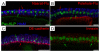
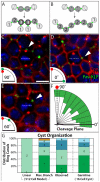
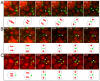
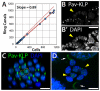
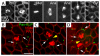
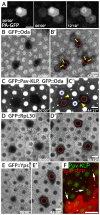
Ring canals connecting Drosophila germline, follicle and imaginal disc cells provide direct contact of cytoplasm between cells. To date, little is known about the formation, structure, or function of the somatic ring canals present in follicle and imaginal disc cells. Here, we show by confocal and electron microscopy that Pavarotti kinesin-like protein and Visgun are stable components of somatic ring canals. Using live-cell confocal microscopy, we show that somatic ring canals form from the stabilization of mitotic cleavage furrows. In contrast to germline cells, syncytial follicle cells do not divide synchronously, are not maximally branched and their ring canals do not increase in size during egg chamber development. We show for the first time that somatic ring canals permit exchange of cytoplasmic proteins between follicle cells. These results provide insight into the composition and function of ring canals in somatic cells, implying a broader functional significance for syncytial organization of cells outside the germline.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong J. D., Texada M. J., Munjaal R., Baker D. A., Beckingham K. M. (2006). Gravitaxis in Drosophila melanogaster: a forward genetic screen. Genes Brain Behav. 5, 222-239 - PubMed
-
- Bauer R., Weimbs A., Lechner H., Hoch M. (2006). DE-cadherin, a core component of the adherens junction complex modifies subcellular localization of the Drosophila gap junction protein innexin2. Cell Commun. Adhes. 13, 103-114 - PubMed
-
- Besse F., Pret A. M. (2003). Apoptosis-mediated cell death within the ovarian polar cell lineage of Drosophila melanogaster. Development 130, 1017-1027 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

